Data protection
Software, use cases & solutions
4.7/5 on Capterra | 2,000+ satisfied customers

What is data protection?
Data protection means: organizations protect personal data in such a way that their processing is lawful, secure, transparent and traceable.
The focus is on clear definitions of purpose, minimal data processing, appropriate protective measures, defined responsibilities and robust evidence. This applies across all sectors and regardless of the size of the company.
In practice, this means that companies must know their data processing, assess risks and implement technical and organizational measures. These include the recording and maintenance of processing activities, data categories and protection requirements, access controls, service providers and processors, erasure and retention concepts, incident handling and regular effectiveness checks.
With the right software, data protection can be mapped in a structured way: from directories and data flows, roles and responsibilities to risks, measures, audits and proof of documentation.
This makes data protection feasible, audit-proof and maintainable in everyday life - without scattered tables, Excel lists or manual isolated solutions.
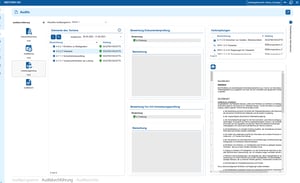
GRC use cases
Use cases relating to ISMS, risk and compliance management

You control audits centrally, plan audits, document results and automatically generate audit reports.

You can manage documents in an audit-proof manner, version and edit them directly in the tool and use templates and import functions.

i-doit supports GAP analyses according to standards such as ISO 27001, ISO 9001 or NIS2, including maturity level assessment, responsibilities and document assignment.

You evaluate and manage suppliers centrally, document contracts and maintain contact details and replacement suppliers.

You derive measures, distribute tasks, track deadlines and receive automatic notifications by e-mail.

You document and evaluate security incidents in accordance with ISO and NIS2, assign affected assets and centrally derive measures.
Data protection as a structured component of the IT organization
Effective data protection is based on complete transparency about where personal data is processed, who is responsible for it and for what purpose. i-doit provides this information in a centralized and structured manner by linking systems, applications, data processing, locations, service providers and responsibilities.
This creates a reliable information base that does not view data protection in isolation, but rather as an integrated component of the IT and process landscape.
Advantages:
- Central overview of IT structures relevant to data protection: processing activities, systems, contracts and responsibilities are consistently documented and can be traced at any time.
- Clear responsibilities: Technical and organizational measures can be clearly assigned to systems, processes and responsible roles.
- Reduced coordination effort: Data protection information is available centrally and does not have to be collected from distributed documents.
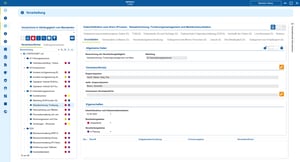
Data protection and IT documentation - linking risks, measures and evidence
Data protection requirements such as TOMs, risk analyses or deletion concepts only develop their value when they are directly linked to the affected systems and processes. Thanks to the structured documentation in i-doit, data protection measures are not described in abstract terms, but are stored specifically for applications, servers, databases or service providers.
This makes it clear which measures apply where, what risks exist and how these are addressed.
Advantages:
- Comprehensible risk assessment: Data protection risks can be assigned directly to the affected systems and data processing.
- Reliable evidence: Technical and organizational measures are documented and can be retrieved in an audit-proof manner.
- Efficient maintenance: Changes to systems or processes automatically affect the associated data protection documentation.
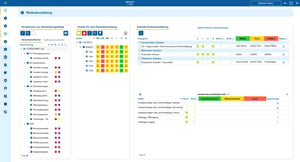
Data protection in the company - information, testing and continuous improvement
During ongoing operations, structured data protection documentation supports the processing of requests for information, internal checks and external audits. As all relevant information is already linked, data flows, storage locations and access authorizations can be traced quickly.
At the same time, the documentation forms the basis for continuous improvement of data protection, for example by identifying unnecessary data processing or outdated systems.
Advantages:
- Fast access to information: Affected requests can be answered efficiently and completely.
- Audit-proof: Data protection-relevant information is consistently documented and can be verified at any time.
- Continuous optimization: Transparency regarding data processing enables targeted reduction of risks and unnecessary complexity.
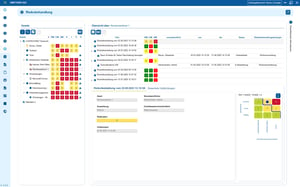
Industries
View all solutions for your industry



Read more



GDPR-compliant in 3 steps
and document it
implement suitable measures
handle professionally
1. Understanding and documenting data processing
Data protection starts with an overview.
Companies need to know which personal data is processed in which systems for which purpose and who is responsible for it.
Without this transparency, every measure is blind. This is why processing, data categories, applications, storage locations, roles and service providers are recorded centrally and linked with each other.
This creates clarity about where data is located, who has access and what dependencies exist.
The aim is not documentation for documentation's sake, but controllability.
Advantages:
- Transparency instead of guesswork: All processing, systems and responsibilities are centrally documented and can be found at any time.
- Practical overview: You know which data is stored where, who has access and on what legal basis it is processed.
- Fast response times: queries from customers, employees or authorities can be answered clearly without having to play "firefighter" within the company.
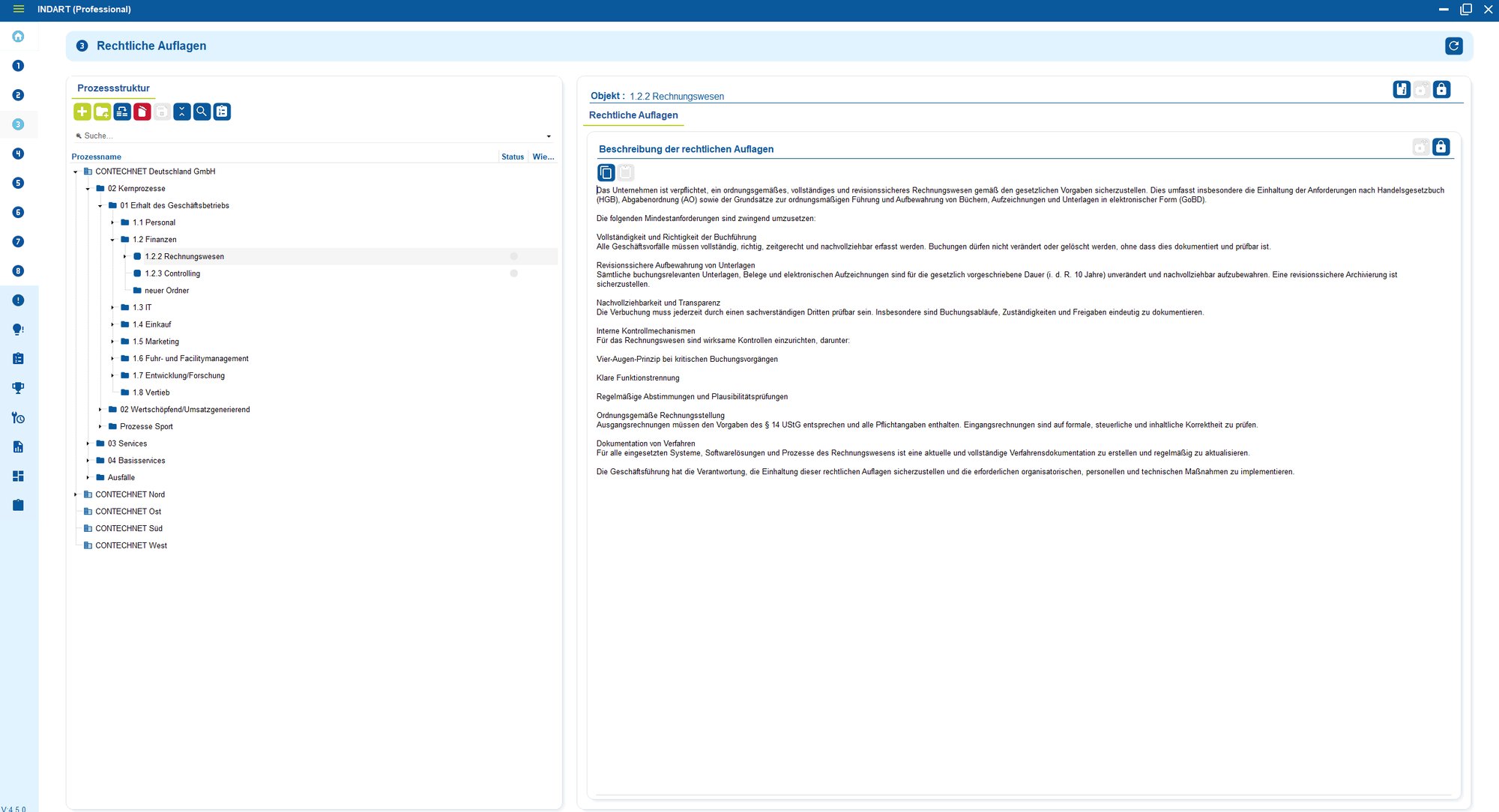
2. Assess risks and implement suitable measures
Not all data processing is equally critical.
Data protection does not mean "securing everything to the maximum", but acting appropriately .
To this end, risks are systematically assessed:
- What impact would an error have on those affected?
- What damage could be caused to the company?
- Where is there a real need for action?
On this basis, measures are specifically derived, prioritized and implemented - not according to gut feeling, but according to risk.
This means that it is always clear why a measure exists, who is responsible for it and whether it works.
This makes data protection plannable, justifiable and controllable.
Advantages:
- Appropriate instead of random security measures: Decisions are based on real risks - not on gut feeling or marketing promises from tool providers.
- Verifiable effectiveness: Every measure has a purpose, a responsible party and a point at which it is checked to see if it works.
- Fewer costly mistakes: Vulnerabilities are identified before the incident - not afterwards when data has already been leaked.
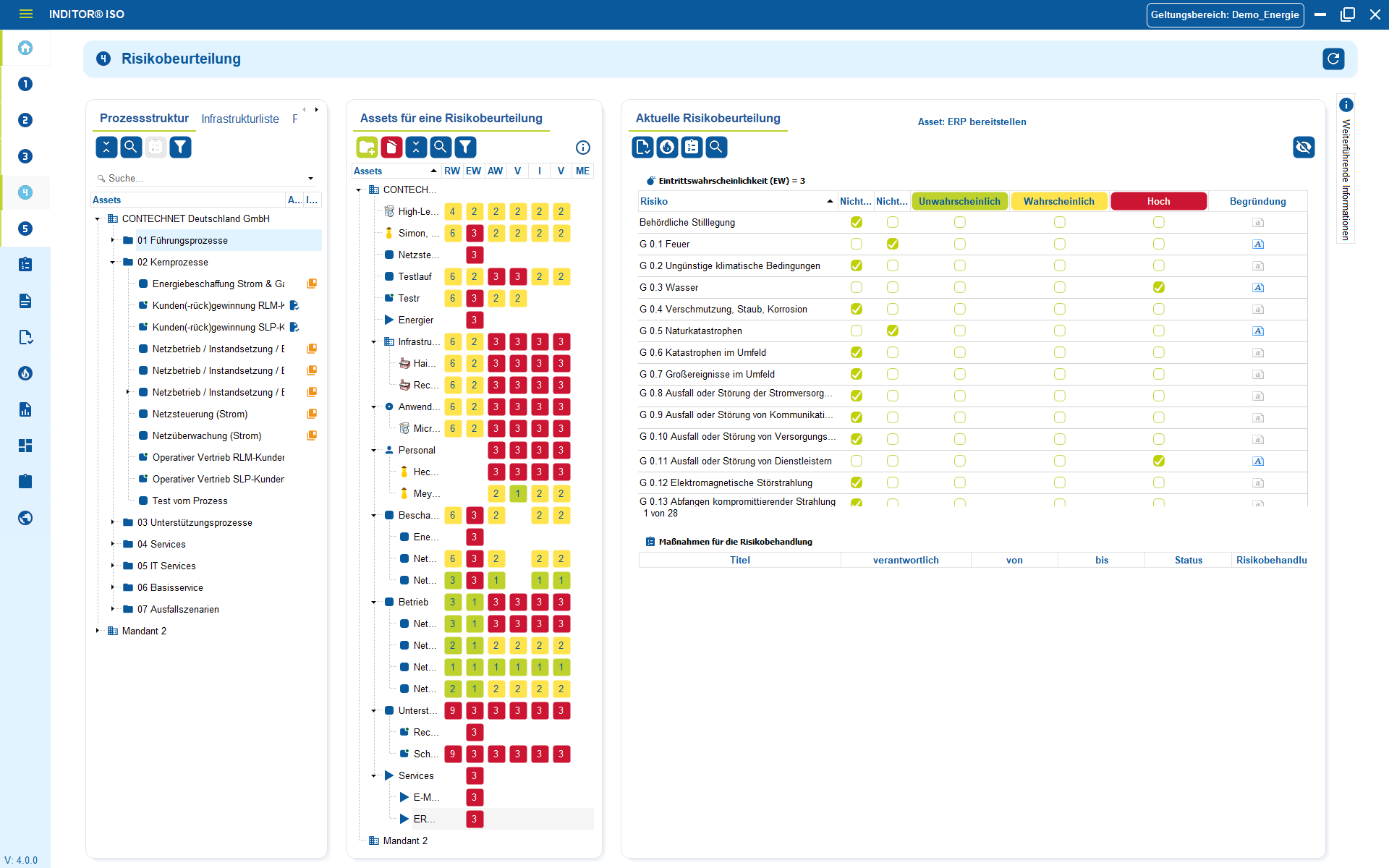
3. Handle incidents and data protection requests professionally
An emergency decides whether data protection works or only exists on paper.
A data incident, an incorrect recipient, a system error or a request from a data subject is never planned, but always time-critical.
Without a clear process, chaos ensues: Who reacts? Who evaluates? Who reports? Who documents?
This is why incidents and requests are recorded, evaluated, processed and closed in a structured manner. Responsibilities, deadlines and decisions are clearly defined and documented in a comprehensible manner.
In this way, companies remain capable of acting, lose no time and retain control.
Advantages:
- Fast response time: Whether an incident or inquiry - there is a defined process, responsibilities and deadlines.
- Proven professionalism: Procedures and decisions are documented - this reduces the risk of sanctions and reputational damage.
- Fewer repeat errors: Every incident provides insights that are incorporated into better measures - real improvement instead of reactive firefighting.
Further use cases for data protection
data processing & systems
and processing guidelines
data subject requests handling
processor control
Control access
1. Import of existing data processing & systems
Information on processing activities, tools, employee data, contracts, CRM systems or external service providers already exists in almost every company - but unfortunately it is completely scattered.
Excel spreadsheets, SharePoint folders, emails, onboarding processes, IT project knowledge - nobody really starts from scratch.
Instead of entering everything from scratch, existing data structures can be adopted, normalized and merged centrally.
The import maps personal data, systems, purposes, roles and responsibilities in an organized manner. The data is classified (e.g. personal data, special categories), responsible parties are assigned and dependencies between processing, system and operator are made visible.
This basis finally provides clarity about where personal data is processed, who has access and what risk arises.
On this basis, measures (Art. 32), DP contracts (Art. 28) and erasure concepts can be assigned without chaos.
Advantages
- No starting from scratch: existing information is transferred instead of having to record everything from scratch.
- Transparency: data flows, responsibilities and access areas become visible.
- Fewer errors: classification, purpose limitation and risk can be assigned directly.
- Auditability: changes are versioned and documented in a traceable manner.
- Future-proof: repeatable imports prevent data silos and duplicate maintenance.
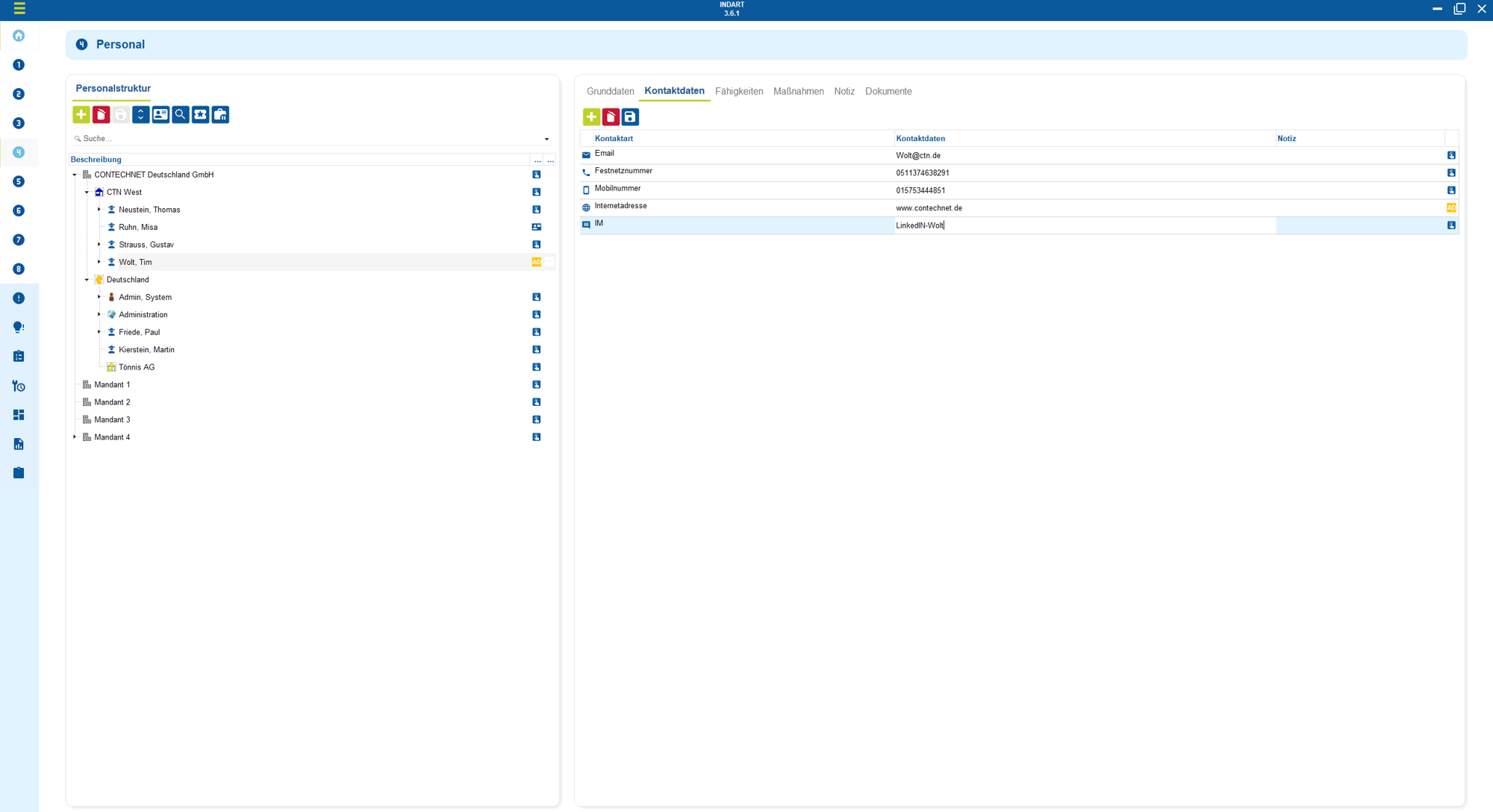
2. Data protection concepts, deletion rules and processing guidelines
In practice, data protection rarely fails due to a lack of rules, but rather because they are not properly implemented on a day-to-day basis.
Deletion periods, roles, access rights, legal bases and storage locations must be clearly defined and traceable in the company. Only then is it clear how personal data is actually processed.
A central solution makes it possible to record and maintain data protection guidelines, deletion concepts, onboarding and offboarding processes and internal processing rules in a structured manner and to link them directly to the actual data processing.
Changes to systems or processes automatically affect the associated documentation. Responsibilities, storage periods, legal bases or exceptions no longer need to be adapted manually in multiple documents.
All content is versioned, checked and linked to people, departments and systems. As a result, data protection remains manageable in day-to-day business and can be checked at any time.
Advantages:
- Centralized and versioned management of policies, deletion rules and procedures
- Changes in systems are taken into account directly in the documentation
- Clear responsibilities thanks to defined persons in charge and review intervals
- Complete traceability of approvals and changes
- Fewer errors thanks to clear guidelines for IT, HR and specialist departments
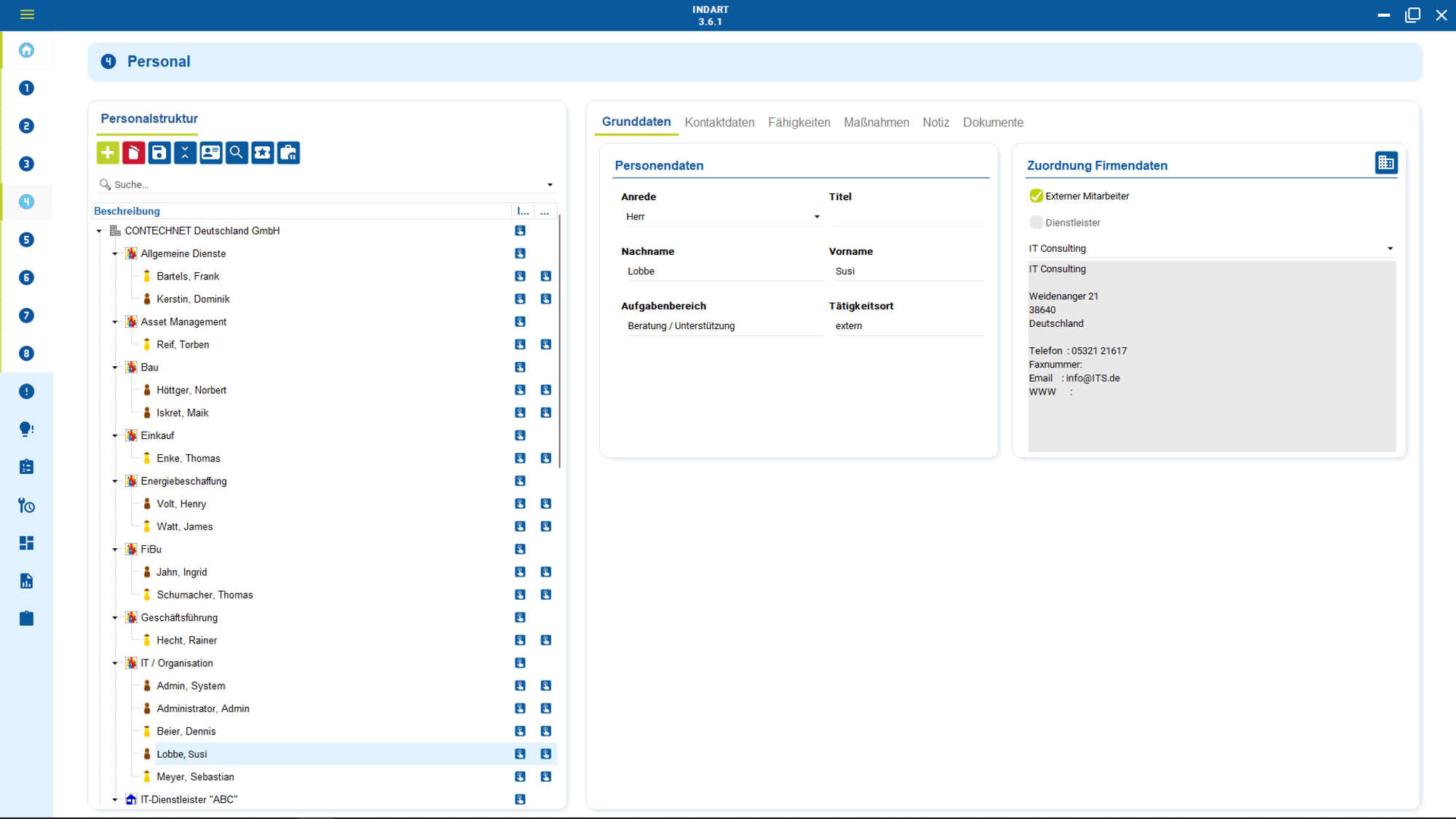
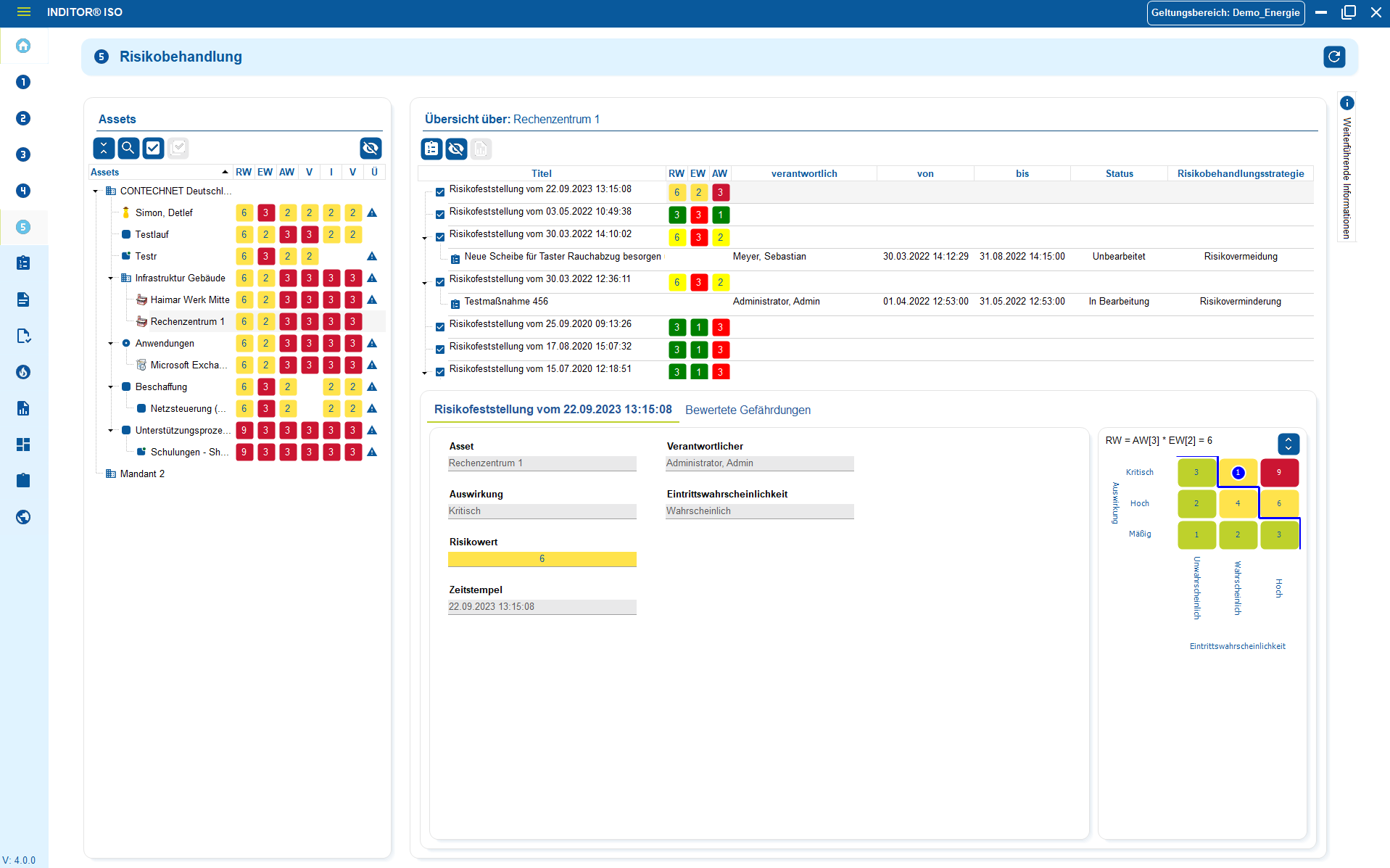
3. Clean handling of data protection incidents & data subject requests
In practice, there are two areas in which data protection regularly causes problems: firstly, data protection incidents such as incorrect recipients, data loss, system errors or unauthorized access. Secondly, data subject requests such as access, erasure, rectification or data portability.
Both issues are time-critical and do not tolerate chaos. Without a clear structure, uncertainty and delays arise. Who reacts. What has been processed. Who is responsible. What needs to be reported.
Centralized incident management ensures that incidents are recorded, evaluated and processed in a structured manner. The incident is assigned to the affected processing activities, systems and responsible parties. Deadlines, measures and decisions are clearly documented.
The same applies to requests for information and deletion. Requests are recorded, checked, answered in accordance with data protection regulations and fully documented. Responsibilities are clearly defined. This ensures that the process remains controllable and traceable. There are no discussions about who is responsible or what to do next.
Advantages:
- Fast and structured processing of incidents and inquiries
- Clear responsibilities and defined processes
- Complete documentation of all decisions and measures
- Reduced risk thanks to correct classification and handling
- Improvements flow directly into processes and measures
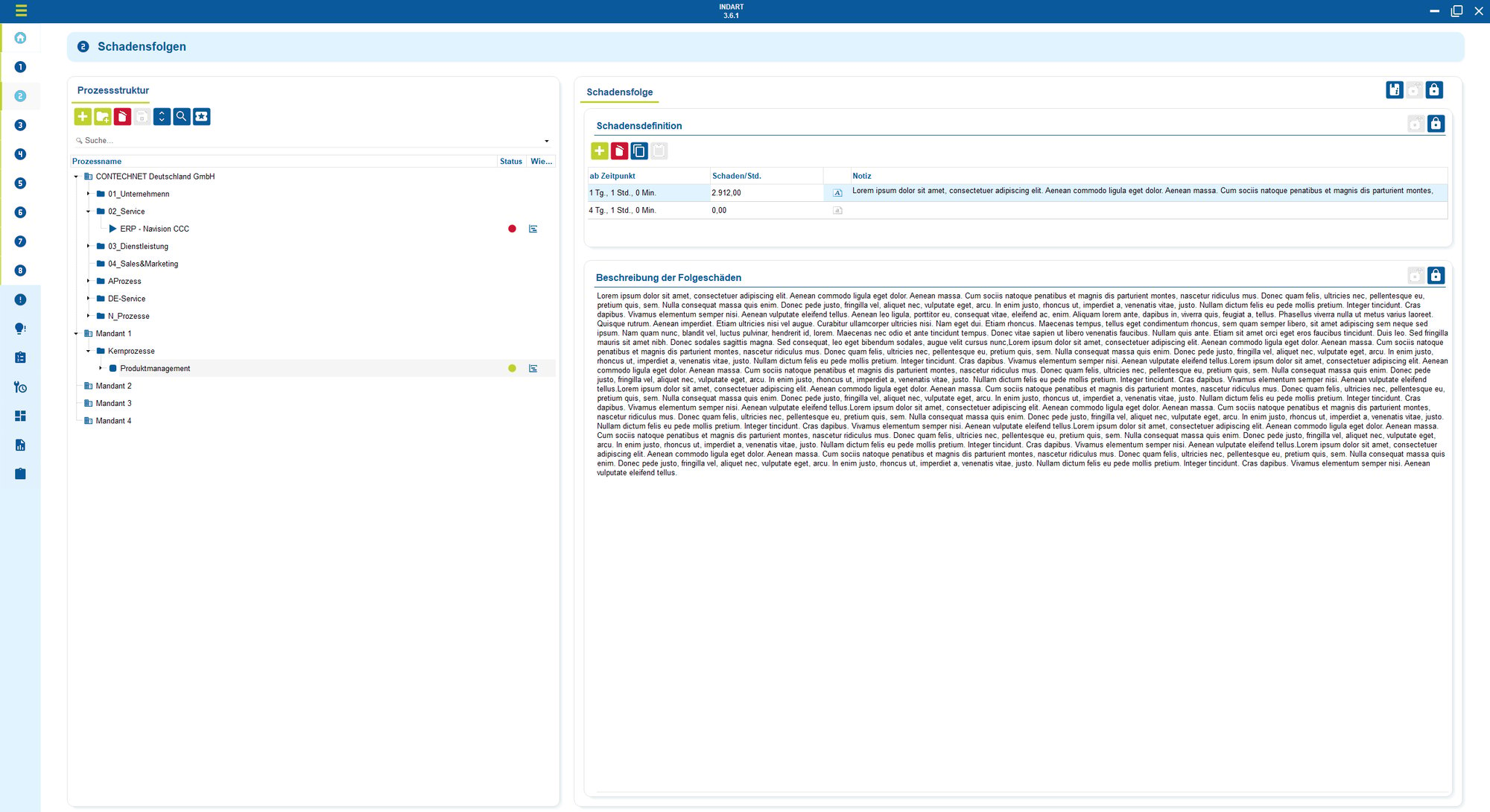
4. Supplier and processor control
The majority of data protection risks do not arise in your own data center, but with external service providers. These include cloud providers, SaaS solutions, hosting partners, HR systems and marketing tools.
Without a clear overview, you quickly lose control. Who processes which data. Where is it stored. Who has access. Which agreements apply.
A central record provides a structured overview of all service providers, contracts, subcontractors and access rights. Responsibilities, processing purposes, data types, locations and dependencies are documented for each provider. The associated agreements and measures are also directly assigned.
This allows companies to retain control over which service provider processes which personal data, for what purpose and under what conditions.
Risks become visible and can be assessed. Critical providers can be prioritized and specifically checked.
Advantages:
- Central overview of all service providers and processors
- Clear assignment of contracts, responsibilities and data types
- Transparency of data flows and storage locations
- Better risk assessment through prioritization according to sensitivity
- Evidence available at any time without lengthy searches

5. Role concepts & controlling access
Data protection only works if there are clear rules on who can access what.
Problems always arise when too many people have too many rights. If everyone can see or change everything, control is no longer possible.
This is why roles, responsibilities and competencies are clearly defined. It is clearly defined who may create or change processing operations, who approves measures and who has access to sensitive information.
Employees only see the data and areas that they need for their tasks. Everything else remains hidden. This creates order instead of uncontrolled growth. Changes are traceable. Errors and escalations are reduced.
Advantages:
- Clear responsibilities without gray areas
- Precise control of rights per data type, system or process
- Protection of sensitive information through restricted access
- Complete traceability of changes
- Fewer errors and more efficient work in the teams
.png?width=300&name=Contact%20(1).png)
Book your personal live demo
Our i-doit team will be happy to take the time to advise you personally on your application.
Integrations
i-doit can be seamlessly connected to IT service desk systems to optimize your support processes. Examples of compatible systems are ((OTRS)) Community Edition, KIX Service Management and Zammad.
Thanks to its flexible API, i-doit can be integrated with numerous software solutions, including ERP systems.
To automatically add data and assets to your i-doit system, we recommend the use of specialized inventory systems such as JDisc or OCS.
With i-doit, you can document your network topology clearly and in detail and include integrations.
For centralized and secure user and rights management, i-doit can be integrated into directory services such as LDAP or Active Directory.
i-doit is made for the joint operation of monitoring systems. Examples here are: Nagios or Checkmk.
Suitable add-ons
Our add-ons for modular function expansion
Create powerful automations without programming knowledge, simply start them on a schedule or manually at the touch of a button.
Get 4 powerful add-ons for the price of 2! Flows, Documents, Analysis and Forms.
Automatically create documents as PDFs with daily updated data (e.g. hardware handover certificate or disaster recovery plan).
Automate the operation of your data center with the latest data from the CMDB. Events trigger and control further processes.
The maintenance add-on supports the planning, execution and documentation of maintenance and inspections. Maintenance intervals, dates and responsibilities are managed centrally and linked directly to the respective devices, installations or systems.
With the API add-on, data can be automatically read, written and updated in i-doit. Perfect for integrations with ticket systems, inventory tools or your own automations.
Add-on for powerful data analysis. Calculate service costs, check the data quality of the CMDB and carry out failure simulations.
Easily create forms that you can make available to users for simplified data entry. Example: Allow users to document hardware or goods themselves.
Set up an information security management system with risk analysis and management in accordance with ISO 27001.
Integrate the Checkmk2 monitoring system into i-doit. This supports comparisons between TARGET and ACTUAL from CMDB and monitoring.
Store buttons with your own triggers and start IT processes directly from i-doit - e.g. the automatic deployment of a virtual machine.
With this add-on, you can create an information security management system (ISMS) in accordance with the BSI's IT baseline protection methodology.




