Emergency management
Software, use cases & solutions
4.7/5 on Capterra | 2,000+ satisfied customers

What is emergency management?
Emergency management describes the ability of an organization to remain capable of acting immediately in the event of technical, physical or organizational failures.
An emergency does not arise from defects alone - it arises when critical dependencies, responsibilities and restart processes are not available.
The foundation for effective emergency management is not a PDF, not a document in SharePoint, not a "concept folder" - but continuously maintained IT documentation that maps systems, people, locations, processes, contracts and recovery paths in relation to each other.
With i-doit, emergency management becomes operational:
- Systems are linked to services
- Services are linked to business processes
- Recovery times (RTO/RPO) are stored technically and organizationally
- Responsibilities, contracts, contact persons and escalation chains are clearly assigned
Automatically updated emergency documentation for various scenarios
GRC use cases
Use cases relating to ISMS, risk and compliance management

You control audits centrally, plan audits, document results and automatically generate audit reports.

You can manage documents in an audit-proof manner, version and edit them directly in the tool and use templates and import functions.

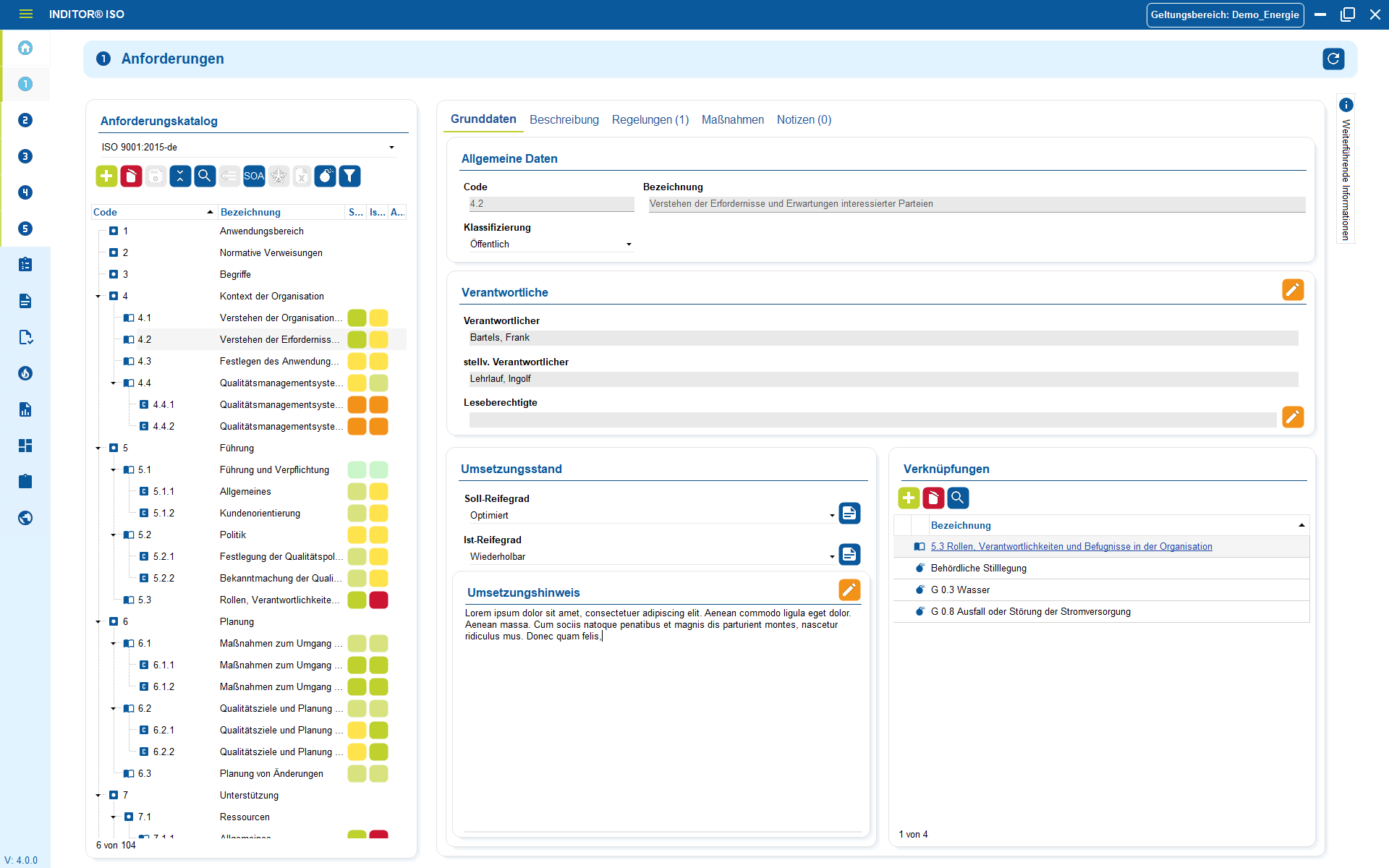
i-doit supports GAP analyses according to standards such as ISO 27001, ISO 9001 or NIS2, including maturity level assessment, responsibilities and document assignment.

You evaluate and manage suppliers centrally, document contracts and maintain contact details and replacement suppliers.

You derive measures, distribute tasks, track deadlines and receive automatic notifications by e-mail.

You document and evaluate security incidents in accordance with ISO and NIS2, assign affected assets and centrally derive measures.
Components of emergency management
Effective emergency management is based on a transparent information base on systems, locations, dependencies, responsibilities and restart processes.
Only if technical and organizational relationships are documented in a comprehensible manner can failures be assessed, prioritized and rectified in a targeted manner.
The combination of infrastructure information, fault data, escalation paths and restart strategies creates a basis that enables action to be taken in an emergency.
Emergency management thus becomes an ongoing process - from risk awareness, preparation and simulation to recovery and evaluation.
Advantages:
- Clear basis for decision-making: Impacts, priorities and responsibilities are visible at all times.
- Shorter restart times: Processes and dependencies are available in a structured manner and do not have to be determined on an ad hoc basis.
- Sustainable stability: findings from incidents flow back into documentation, processes and prevention.
Good IT documentation shows the relationships and dependencies between systems, applications, contracts, people and other assets for emergency management on other assets
Development of an ISMS
Structure, responsibilities and measures
An information security management system (ISMS) only works if processes, risks and responsibilities are not documented in the abstract, but in an operational context. With INDITOR, business processes, technical assets and security measures are logically linked - from risk analysis to evaluation and implementation control.
Risks are not "listed in Excel", but assessed directly at the affected systems, locations or services.
Technical and organizational measures (TOMs) are assigned in a traceable manner and can be versioned across audits, reviews or changes. Responsibilities, deadlines and effectiveness are visible in day-to-day business instead of just in the audit report.
Advantages:
- Real audit capability instead of paper processes
- Transparent measures and responsibilities per asset and process
- Audit-proof history - traceable at any time
- The basis for ISO 27001, NIS2 and KRITIS tickets can be linked directly to assets in i-doit in order to list all associated processes in a structured manner.

Emergency plan
Restoration structured and auditable
An emergency plan is only useful if it functions independently of people and enables immediate action in the event of an emergency.
INDART maps emergency processes along real infrastructure: priorities, restart sequences, contacts, replacement paths and decision rules are clearly structured and linked to the affected assets.
This makes it possible to plan for emergencies:
- Restart times (RTO/RPO) are based on business impact rather than gut feeling.
- Fallback options, roles, communication channels and workarounds are documented and can be called up at any time.
- Real events, tests and simulations flow back into the plan and make it significantly more robust via iterations.
Advantages:
- Certainty of action under time pressure
- Reduced restart times thanks to clear sequences
- Minimized risk of wrong decisions or loss of knowledge
- Continuous improvement through documented exercises and incidents
Devices are regularly scanned using inventory and discovery tools and automatically transferred to the IT documentation.
Monitoring
Operating states and events in the context of documentation
Monitoring systems determine the status of systems and services in real time. Thanks to the link with i-doit, these statuses are not viewed in isolation, but in the context of the documented assets.
Warnings, threshold values and availabilities therefore relate to specific devices, servers, applications or network segments. The collected status information supplements the documentation and forms a reliable basis for planning, troubleshooting and service quality.
Advantages:
- Current operating data visible on the affected assets
- Identification of faults with reference to locations or dependencies
- Conclusions about bottlenecks or recurring faults
- Support for trend analyses, maintenance cycles and capacity planning
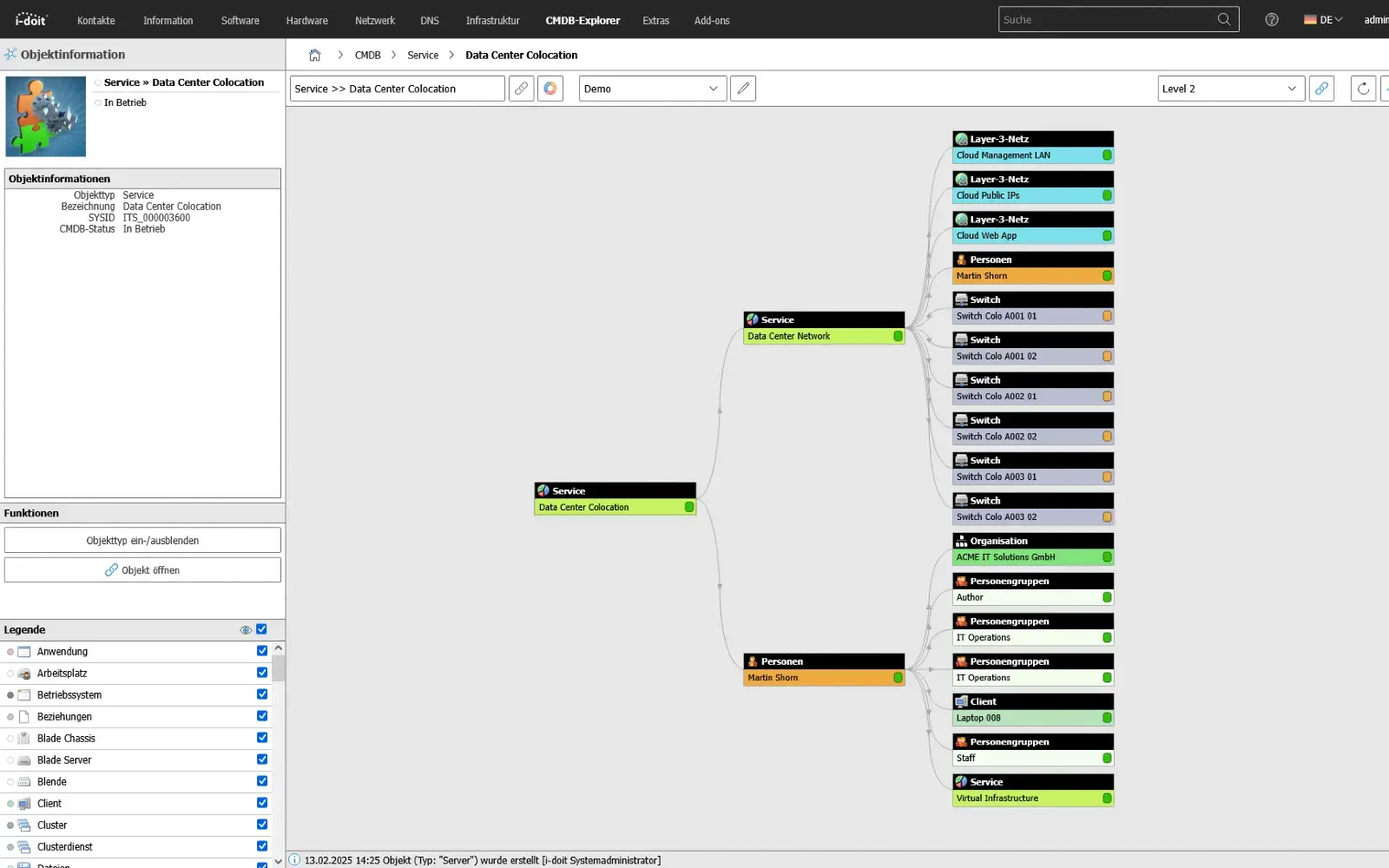
With the CMDB Explorer, you can see all existing relationships and dependencies for all assets.
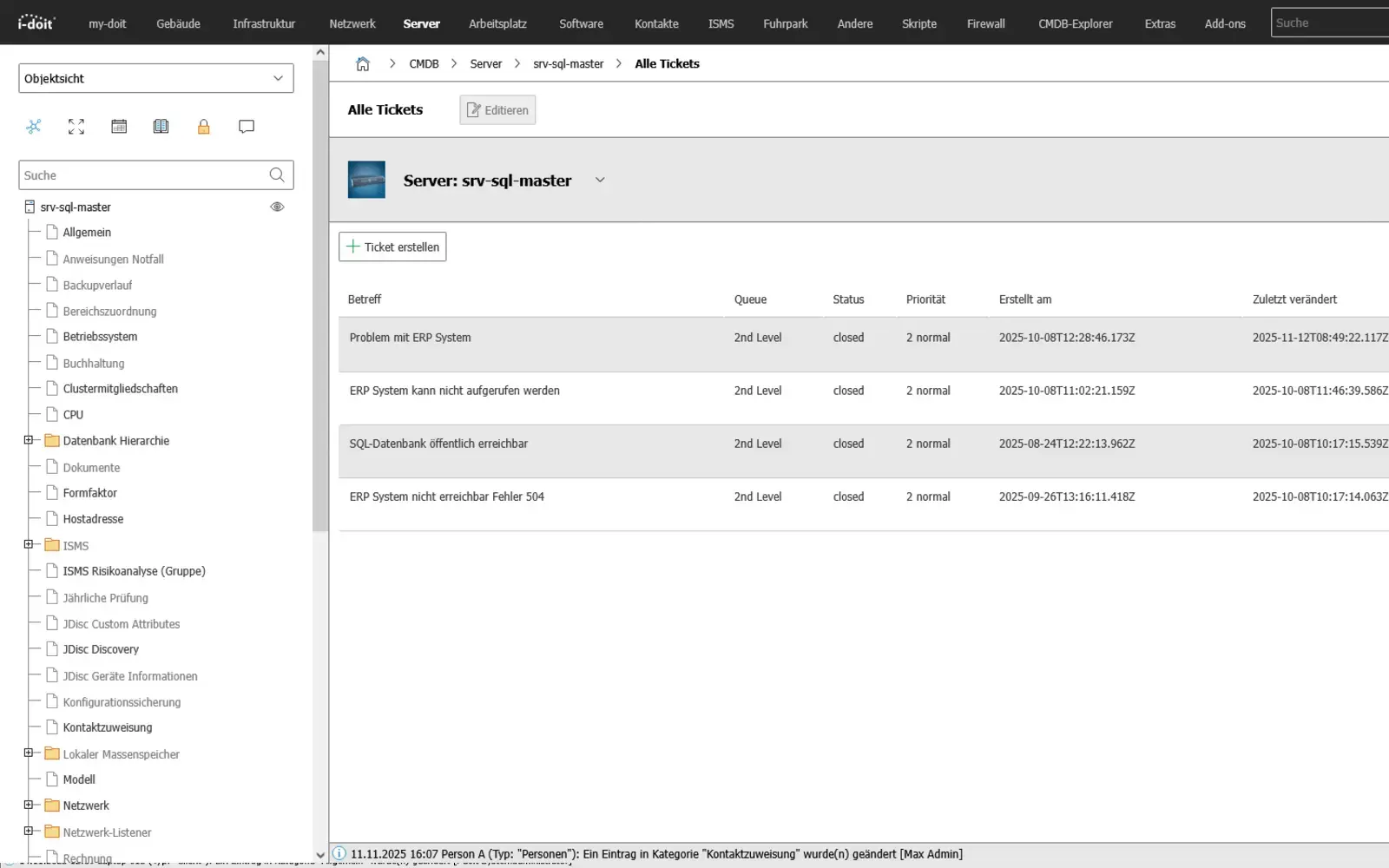
Ticketing
Link processes, faults and tasks directly to assets
By connecting a ticket system, i-doit becomes the central source of information for IT support. When a ticket is created, all relevant data on the affected device, user or service is immediately available - including history, faults, software versions and contracts. Processes can be linked directly to the associated assets so that support and technology work with the same database. The bidirectional exchange automatically keeps all information up to date and reduces manual effort.
Advantages:
- Faster error analysis: All relevant asset and user information is directly available with the ticket, which means that causes can be identified more quickly.
- Standardized information: Support, technology and management work with the same database thanks to the direct linking of tickets and CMDB objects.
- Automated up-to-dateness: Bidirectional synchronization keeps master data, status and changes up to date without manual effort.
Tickets can be linked directly to assets in i-doit in order to list all associated processes in a structured manner.
Industries
View all solutions for your industry



Read more



How to set up centralized emergency management
and priorities
and escalation paths
and improve
1. Record critical systems, dependencies and priorities
The first step is to identify all business-relevant systems and processes and document their dependencies. This includes technical components, user groups, locations, interfaces and suppliers - including their impact on business processes.
This transparent mapping creates clear priorities for recovery and emergency operation: which systems can be operated first, which later and which can be operated alternatively without jeopardizing overall operations.
2. Define restart strategies, roles and escalation paths
In the second step, specific measures are defined for different scenarios. These include recovery sequences, fallback options, responsibilities, deputies and communication channels.
Instead of abstract documents, practicable instructions are created that work independently of individuals: Who decides who is informed, what sequence is followed and what limits stop or continue emergency operations.
3. simulate, document and improve emergencies
In the final step, the defined processes are regularly tested - realistically and under time pressure. Every exercise or actual event is recorded: Sources of error, delays, information gaps or organizational barriers flow back into the emergency plan.
Emergency management thus becomes a continuous process that evolves with the infrastructure, responsibilities and operational requirements instead of remaining a static document.
Further use cases for the use of IT asset management
(KRITIS, ISO27001 and NIS2)
third-party systems (API)
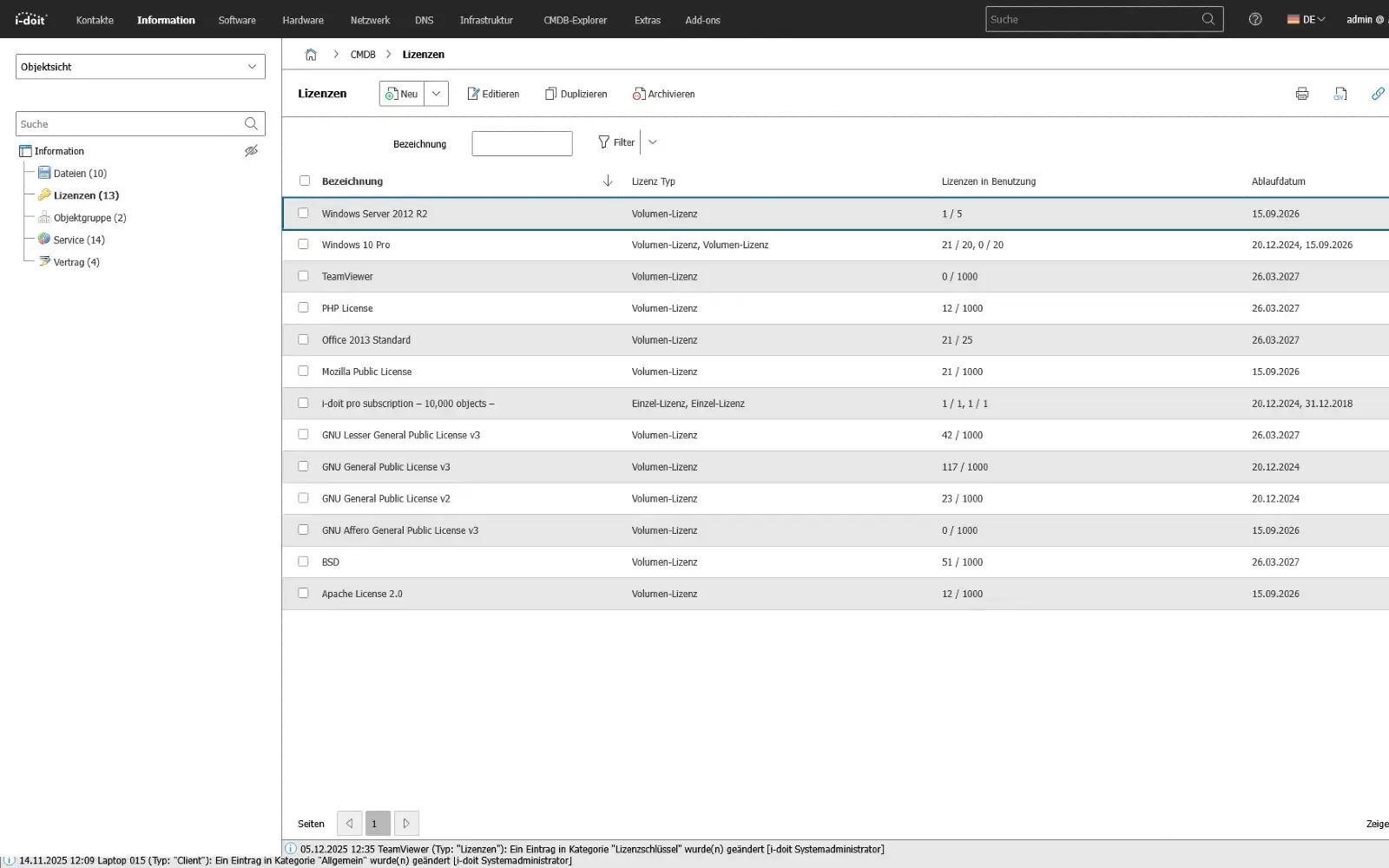
license management
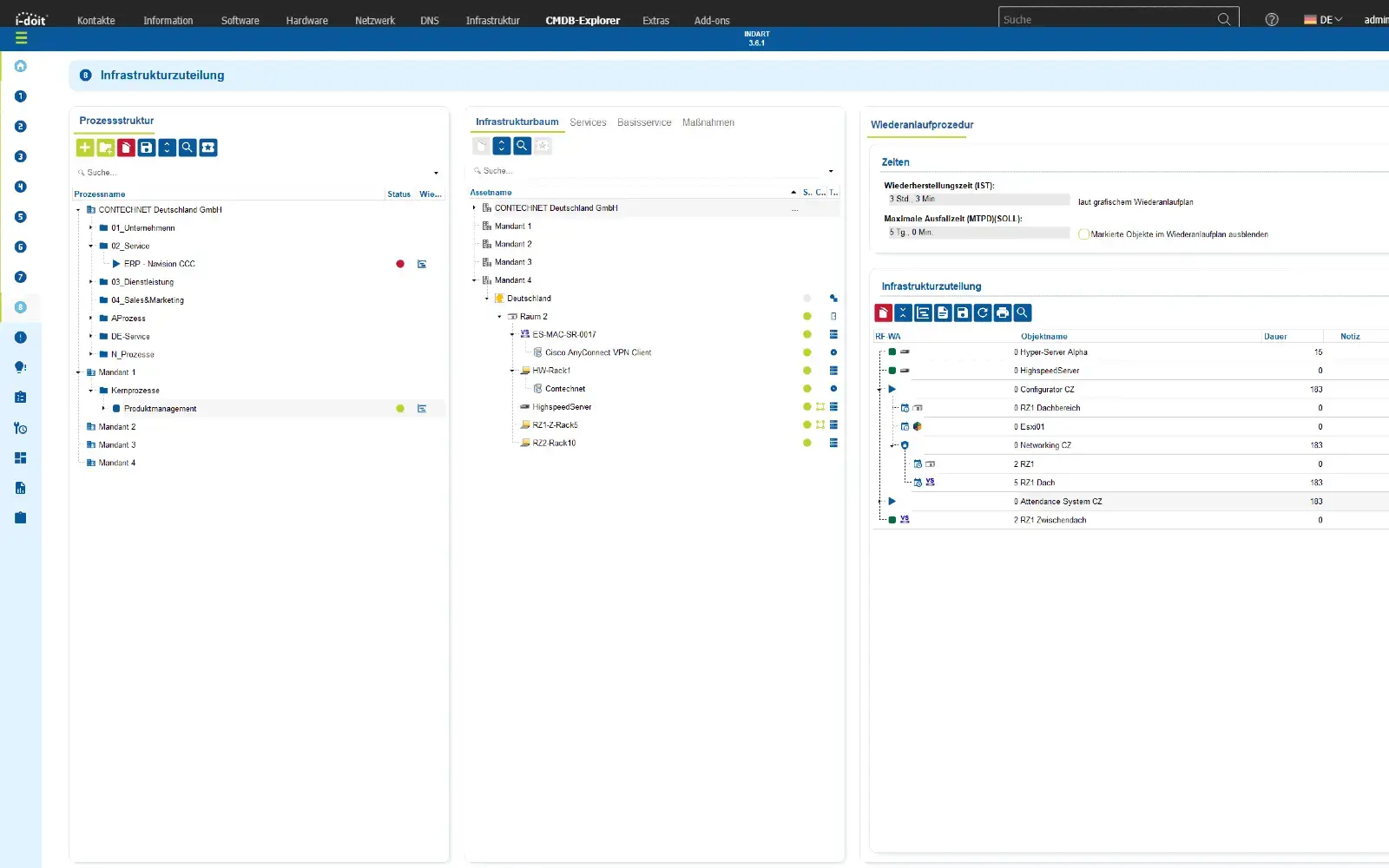
1. Maintain compliance (KRITIS, ISO27001 and NIS2)
Ensure compliance with laws, standards and directives with a CMDB.
With i-doit, risks according to ISO 27001 can be systematically recorded, evaluated and linked to the affected assets. This creates a transparent basis for the verification of security measures and the implementation of NIS2 requirements. Technical and organizational measures (TOMs) are centrally documented, monitored and maintained in an audit-proof manner.
Advantages:
- Auditable company divisions
- Audit-proof recording in accordance with NIS2 & ISO-27001 & BSI-KritisV
- Strengthening of information security,
- Implementation of PDCA processes
- Faster response in the event of an incident or crisis
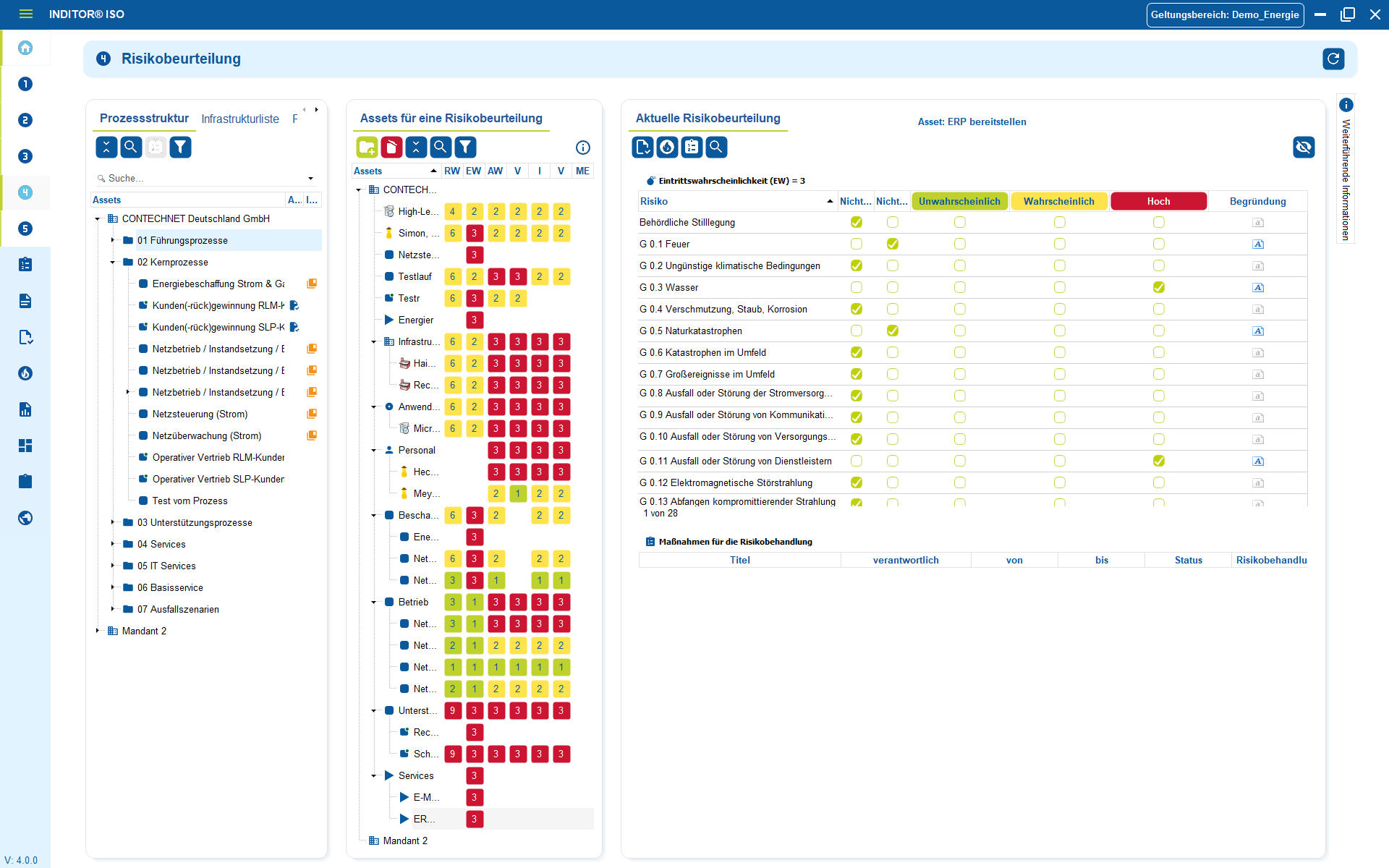
2. Site management
Locations, buildings and rooms form the physical basis of every IT infrastructure and therefore also of every emergency management system.
Structured documentation makes it possible to clearly assign server rooms, data centers, network segments, systems and workstations and to understand their function in the overall operation.
By linking systems, dependencies and responsibilities with specific locations, a realistic picture of the operating environment is created.
In the event of an emergency, it is immediately clear which components are affected, which areas need to be prioritized and what alternatives are available - such as alternative areas, spare rooms or redundant infrastructure.
All relevant site information such as premises, access rules, supply interfaces, cabling routes or environmental parameters can be recorded centrally and versioned.
This ensures that physical risks - for example power failure, line damage, fire or climate problems - are not assessed and addressed theoretically, but on the basis of actual conditions. he documentation is not only maintained, but actively lived and constantly kept up to date. This is one of the most important factors for audits, certifications and operational stability.
Advantages:
- Transparent mapping of physical infrastructure and its dependencies
- Clear assignment of systems and responsibilities per location
- Quick assessment of the effects of disruptions or failures
- Basis for restart strategies, evacuation routes and replacement locations
- Standardized information for operations, safety, technology and management
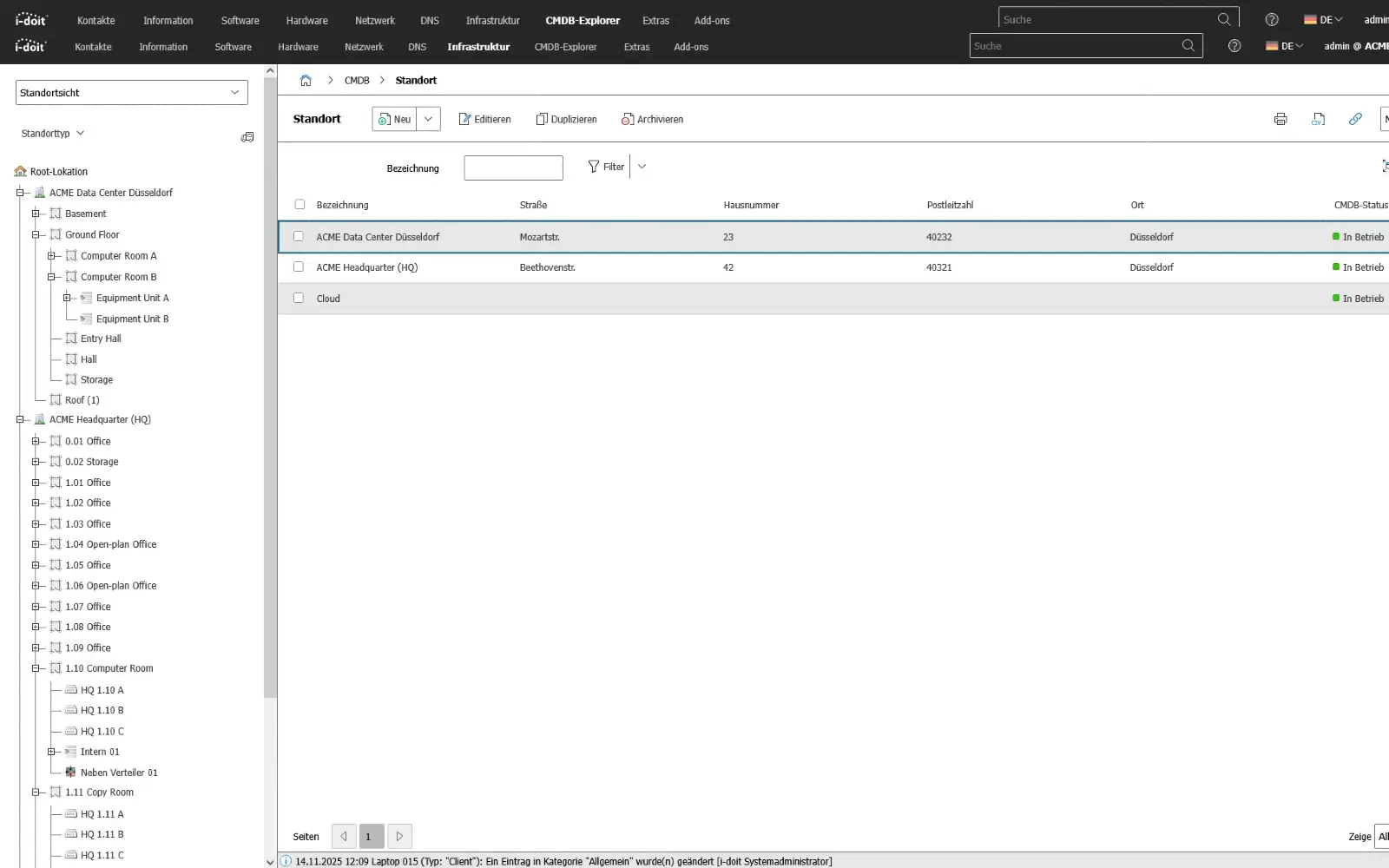
3. Connection of third-party systems (API)
Connect systems automatically and exchange data seamlessly between applications.
With the i-doit API, you can seamlessly connect your CMDB to existing applications, services and automations. Whether ticketing, monitoring, discovery, asset management or your own business tools: Data can be exchanged bidirectionally, updated and processed in real time. This creates a central information point that connects different systems with each other and considerably simplifies processes.
Configurations, status values, object data and relationships can be automatically transferred to or from external systems. Changes made in a connected system can be immediately mapped in the CMDB - without manual effort and without duplicate data storage.
The API enables companies to flexibly expand their processes, automate workflows and make information available exactly where it is needed.
Advantages:
- Automatic data exchange between CMDB and third-party systems
- Bidirectional synchronization of assets, status values, relationships and metadata
- No duplicate maintenance thanks to a central, standardized data source
- Flexible integration into existing software landscapes and specially developed tools
- Automation of processes (e.g. creation of new tickets, discovery updates, monitoring alerts)
- Higher data quality, as information is always kept up-to-date and consistent
- Optimal basis for processes, reporting, audits and ITSM workflows
4 Software and license management
Software, license and certificate information is crucial in an emergency because it enables or blocks the operation of applications, services and business processes.
Structured documentation creates transparency about which systems use which software, which dependencies exist and which license periods or certificates influence access or operation.
By linking versions, installations, user groups and contractual conditions, it is possible to immediately identify the impact of a failure, update or license expiry on operations.
Risks such as loss of functionality, license violations, manufacturer dependencies or missing support authorizations become visible at an early stage and can be taken into account in emergency scenarios.
All software-related information - from installation paths, recovery keys and update histories to maintenance contracts and end-of-life data - can be maintained and versioned centrally.
This means that recoveries, migrations and switchovers can be carried out securely and reproducibly without being dependent on individual knowledge or spontaneous decisions.
Advantages:
- Transparent overview of deployed software, versions and license status
- Early detection of risks due to expiration dates, dependencies or manufacturer support
- Clear reference between applications, services and affected user groups
- Realistic planning of recoveries and emergency operating strategies
- Traceable history for audits, changes and incident analyses
5. Disruption management
Disruptions in production and supply chains rarely occur in isolation. They affect the entire process chain - from systems in individual rooms to preliminary stages, transport routes and downstream production steps.
By displaying equipment status, room plans and dependencies, effects can be localized immediately: If a machine is faulty, all connected areas, processes and components are visible - including the people who are responsible.
The history of maintenance work carried out, replacement components and fault patterns is maintained directly on the affected resources.
This creates traceable processes: when the fault occurred, who intervened, which measures were effective and which preventative steps need to be planned for the future.
Especially in production lines or linked supply chains, this transparency shortens reaction times and prevents secondary faults that would otherwise only become visible at a late stage
Advantages:
- Immediate visibility of technical problems in the real context of rooms, systems and process steps
- Traceable causes and effects along the entire supply or production chain
- Seamless maintenance history as a basis for prevention, QA and audits
- Reduced downtimes thanks to clear responsibilities and documented measures
- Early detection of pattern errors, bottlenecks or recurring faults
.png?width=300&name=Contact%20(1).png)
Book your personal live demo
Our i-doit team will be happy to take the time to advise you personally on your application.
Integrations
i-doit can be seamlessly connected to IT service desk systems to optimize your support processes. Examples of compatible systems are ((OTRS)) Community Edition, KIX Service Management and Zammad.
Thanks to its flexible API, i-doit can be integrated with numerous software solutions, including ERP systems.
To automatically add data and assets to your i-doit system, we recommend the use of specialized inventory systems such as JDisc or OCS.
With i-doit, you can document your network topology clearly and in detail and include integrations.
For centralized and secure user and rights management, i-doit can be integrated into directory services such as LDAP or Active Directory.
i-doit is made for the joint operation of monitoring systems. Examples here are: Nagios or Checkmk.
Suitable add-ons
Our add-ons for modular function expansion
Create powerful automations without programming knowledge, simply start them on a schedule or manually at the touch of a button.
Get 4 powerful add-ons for the price of 2! Flows, Documents, Analysis and Forms.
Automatically create documents as PDFs with daily updated data (e.g. hardware handover certificate or disaster recovery plan).
Automate the operation of your data center with the latest data from the CMDB. Events trigger and control further processes.
The maintenance add-on supports the planning, execution and documentation of maintenance and inspections. Maintenance intervals, dates and responsibilities are managed centrally and linked directly to the respective devices, installations or systems.
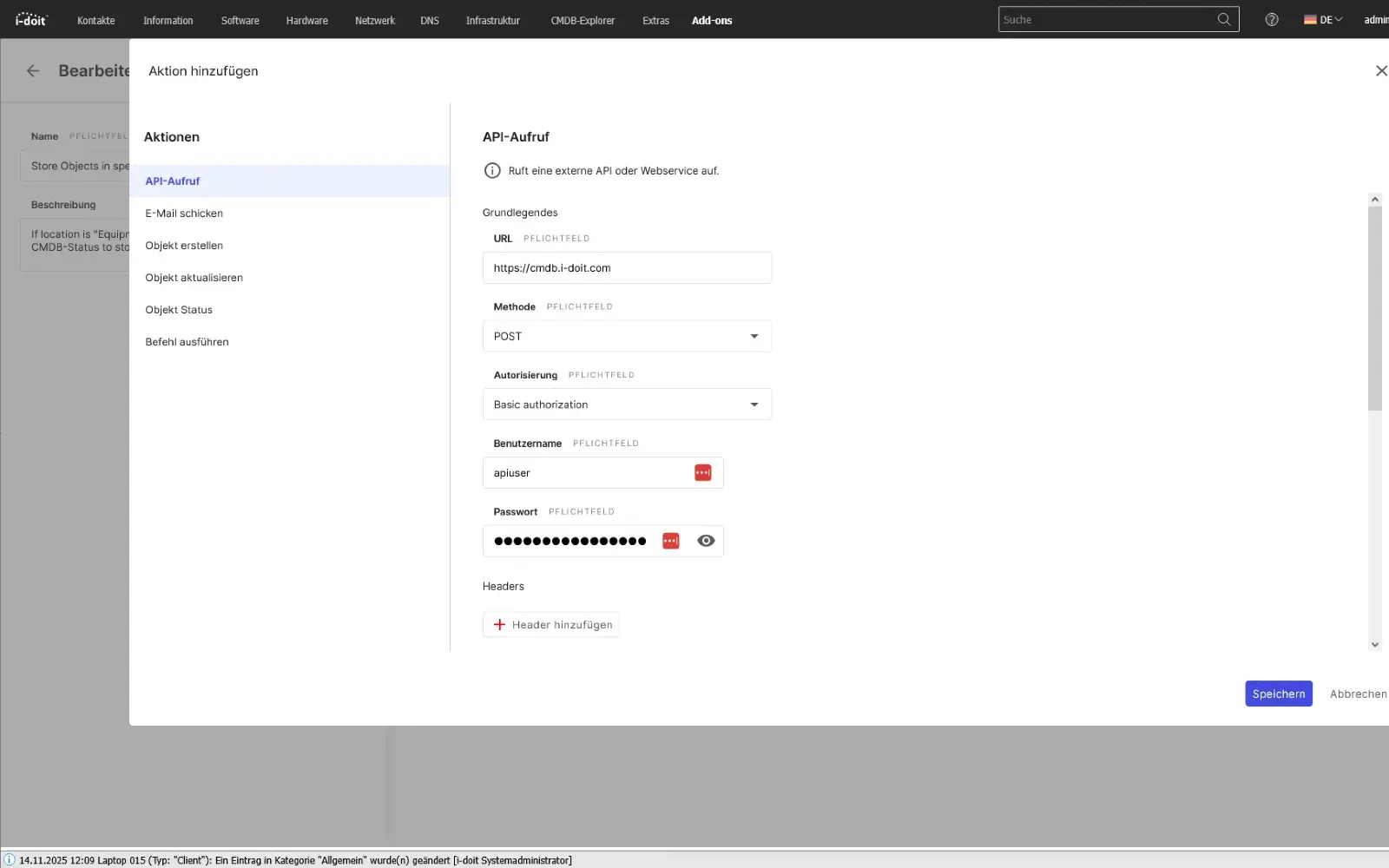
With the API add-on, data can be automatically read, written and updated in i-doit. Perfect for integrations with ticket systems, inventory tools or your own automations.
Add-on for powerful data analysis. Calculate service costs, check the data quality of the CMDB and carry out failure simulations.
Easily create forms that you can make available to users for simplified data entry. Example: Allow users to document hardware or goods themselves.
Set up an information security management system with risk analysis and management in accordance with ISO 27001.
Integrate the Checkmk2 monitoring system into i-doit. This supports comparisons between TARGET and ACTUAL from CMDB and monitoring.
Store buttons with your own triggers and start IT processes directly from i-doit - e.g. the automatic deployment of a virtual machine.
With this add-on, you can create an information security management system (ISMS) in accordance with the BSI's IT baseline protection methodology.




