NIS-2
Software, use cases & solutions
4.7/5 on Capterra | 2,000+ satisfied customers

What is the NIS2?
Introduction
The NIS-2 Directive is an EU-wide guideline for strengthening cyber security in companies and organizations.
It defines how cyber risks must be identified, assessed and handled and how security measures must be implemented and verified.
The aim is to permanently ensure the availability, integrity and confidentiality of network and information systems.
The requirements of NIS-2 can be implemented in a structured and auditable manner using suitable tools.
NIS-2 creates a binding framework for:
- the structured handling of cyber risks
- clearly defined responsibilities and processes
- comprehensible security measures
- reliable evidence for the authorities

Use cases
Use cases relating to ISMS, risk and compliance management

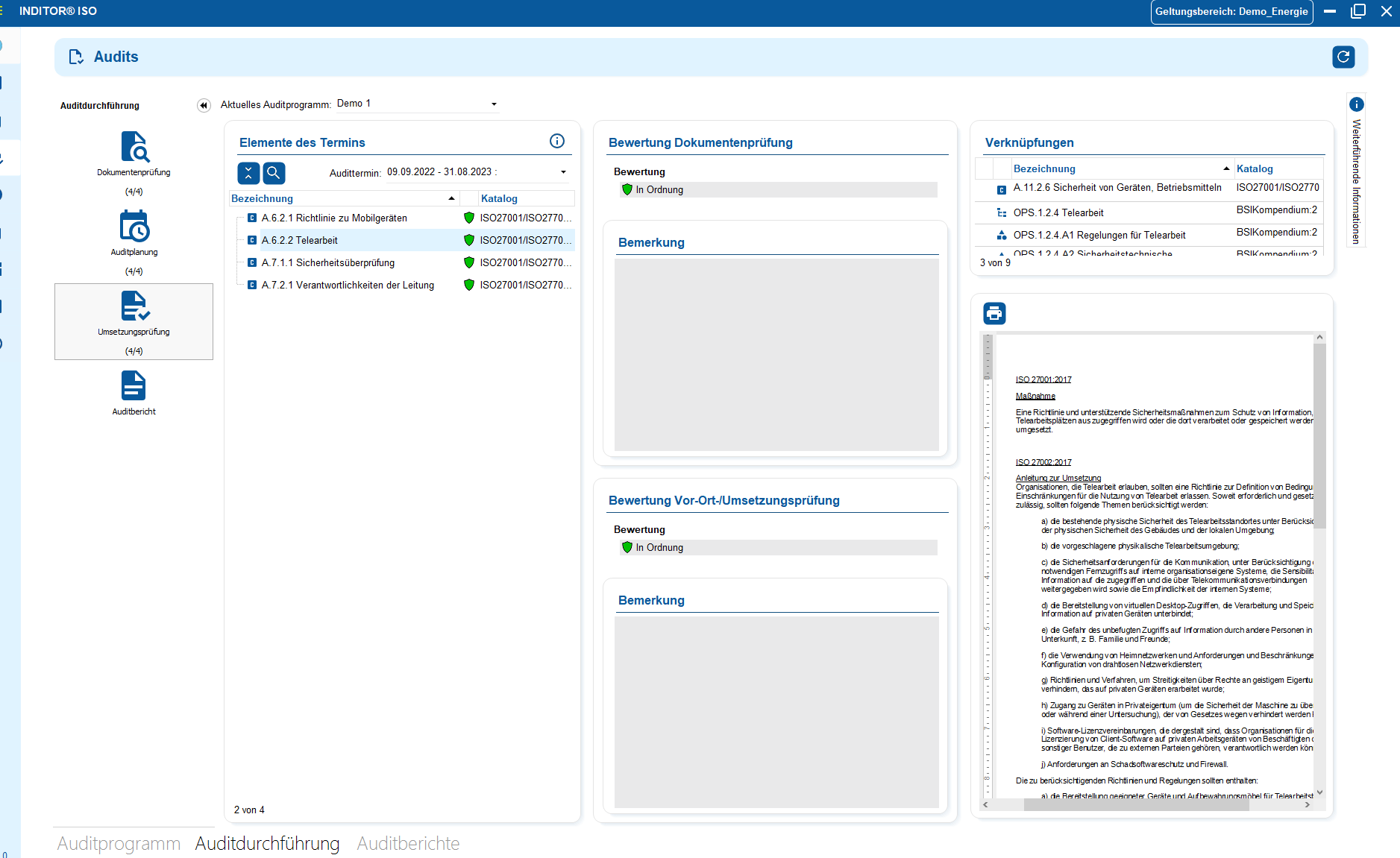
You control audits centrally, plan audits, document results and automatically generate audit reports.

You can manage documents in an audit-proof manner, version and edit them directly in the tool and use templates and import functions.

i-doit supports GAP analyses according to standards such as ISO 27001, ISO 9001 or NIS2, including maturity level assessment, responsibilities and document assignment.

You evaluate and manage suppliers centrally, document contracts and maintain contact details and replacement suppliers.

You derive measures, distribute tasks, track deadlines and receive automatic notifications by e-mail.

You document and evaluate security incidents in accordance with ISO and NIS2, assign affected assets and centrally derive measures.
Why ISMS?
Why an information security
management system forms the basis
Why ISMS?
Companies that fall under NIS-2 often do not have a central overview of security risks, responsibilities and relevant processes.
However, NIS-2 requires a structured management system. An ISMS uniformly maps risks, processes, measures and responsibilities and creates the basis for comprehensible implementation and evidence.
Advantages:
- Clear entry: Structured model for risks, measures, protection requirements, responsibilities and documents - without scattered Excel lists or heterogeneous filing systems.
- Complete traceability: Every decision, test, effectiveness assessment and change is versioned and historicized - a core element of NIS2 compliance.
- Process support in accordance with NIS2: Risk analysis & treatment, business continuity (BCM) and supplier & incident management are integrated and systematically controllable.
Each requirement of the standard is managed as a separate data record - with responsible persons, maturity level, implementation instructions and relevant links.
3 steps to an ISMS
recognize risks
and verify
manage
1. identify critical functions and risks
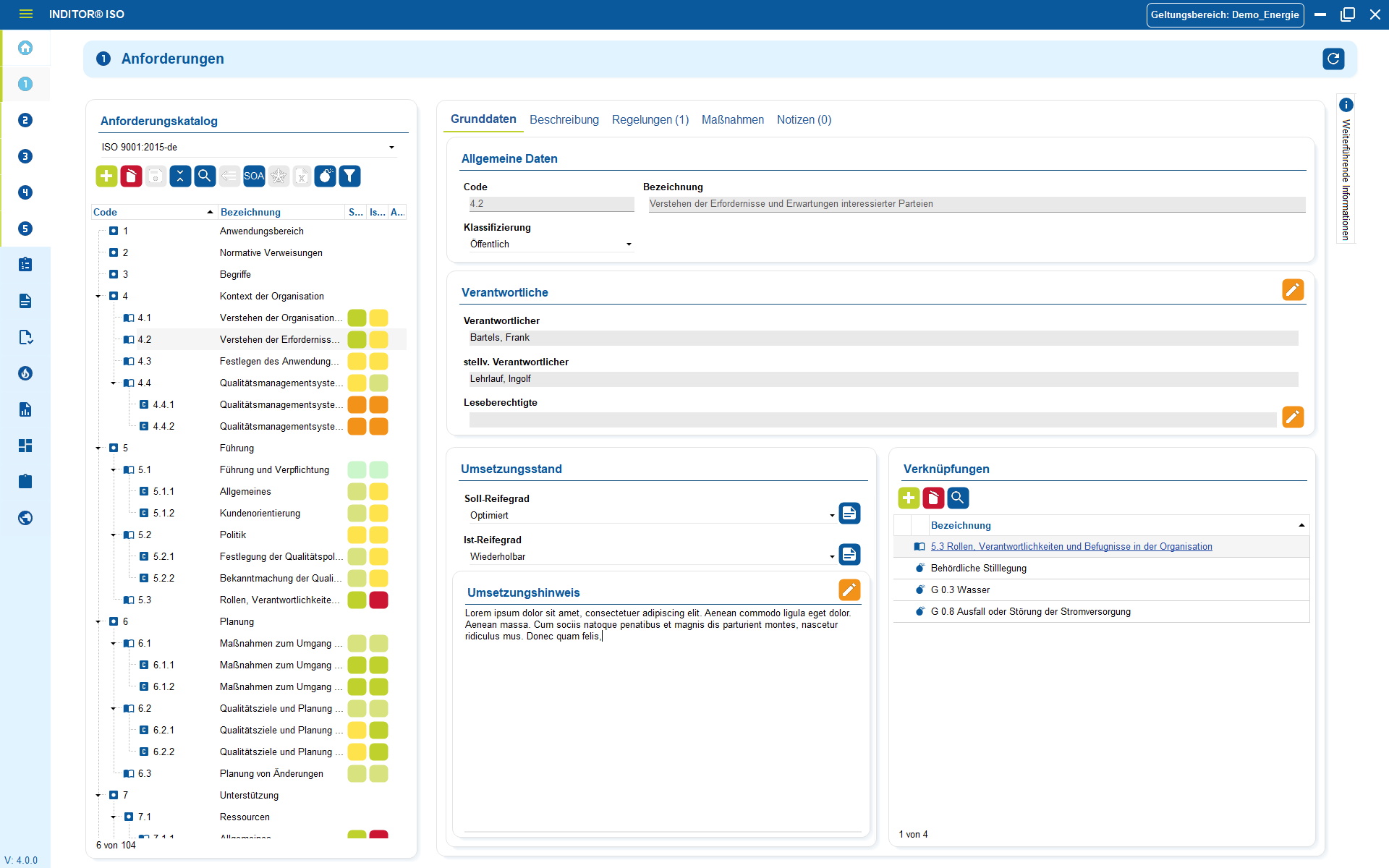
KRITIS operators need to know which systems and components they use, where they are located, what function they fulfill in the supply, what protection requirements exist and what risks arise from them.
Our solutions fully map these requirements by centrally recording, structuring and logically linking all relevant information values - from systems, networks and applications to locations, operating processes and service providers through to roles and responsibilities. On this basis, the risk analysis can be carried out in a targeted manner.
Threats, vulnerabilities and effects are applied directly to the respective objects so that the risk assessment does not remain abstract, but is carried out specifically on the basis of the real system and process landscape .
Advantages:
- Asset management: All relevant system components, operating processes and responsibilities are recorded in a complete, structured and verifiable manner.
- Risk analysis on the object: Threats, vulnerabilities and effects can be assessed directly on assets, processes or critical functions - not in tables or Excel lists.
- Assignable measures: Technical and organizational measures (TOMs) can be assigned directly to the affected assets, risks or processes.
- Integrated determination of protection requirements: Criticality, confidentiality, integrity and availability are assessed centrally and are automatically incorporated into risk and action decisions.
2. plan, implement and demonstrate measures
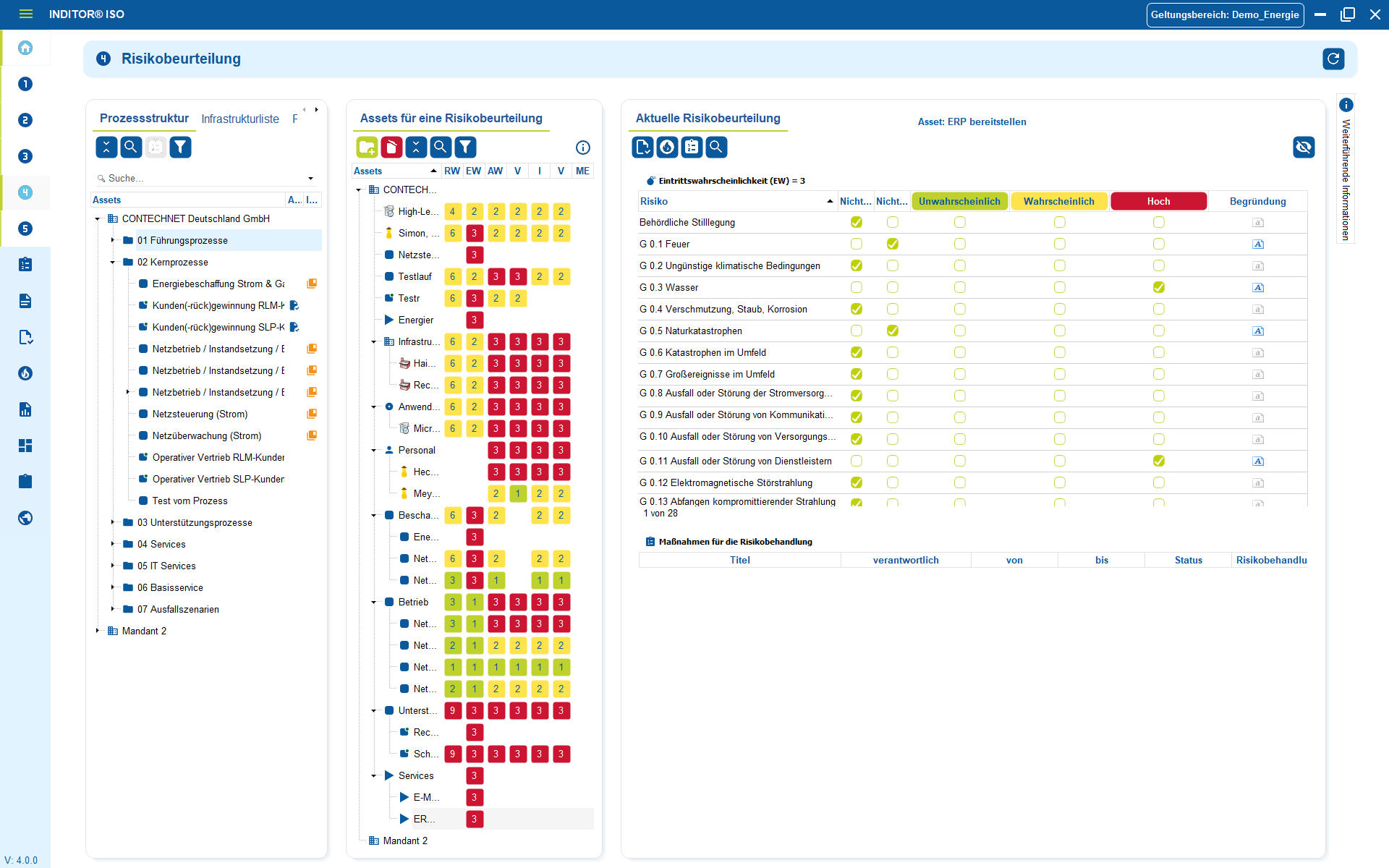
Under NIS2, identified risks and vulnerabilities must be addressed through appropriate technical and organizational measures (TOMs) . Measures must be appropriate, effective, prioritized and documented - along the actual business processes, systems and external dependencies.
Structured measure management fully maps this process:
Measures are recorded centrally, assigned to the relevant risks, systems or processes and documented in an audit-proof manner.
This means that it is always possible to see which measures have been implemented, checked, adapted or are still open - and what effect they have on the risk and threat profile.
Advantages:
- NIS2-compliant measure management: technical and organizational measures are systematically recorded, prioritized and implemented - instead of being a non-binding list.
- Audit-proof documentation: Every change, evaluation and effectiveness check is historicized - verifiable for internal audits and official inspections.
- Responsibilities & deadlines integrated: Each measure is assigned responsible parties, due dates and status; escalations in the event of delays are possible and can be documented.
- Proof of effectiveness: Measures are not only defined, but also regularly checked for effectiveness - including adjustments and lessons learned.
- Direct link to assets & risks: Measures are attached to real systems, processes or supply chains - not abstract or isolated.
3. manage policies and procedures in an audit-proof manner
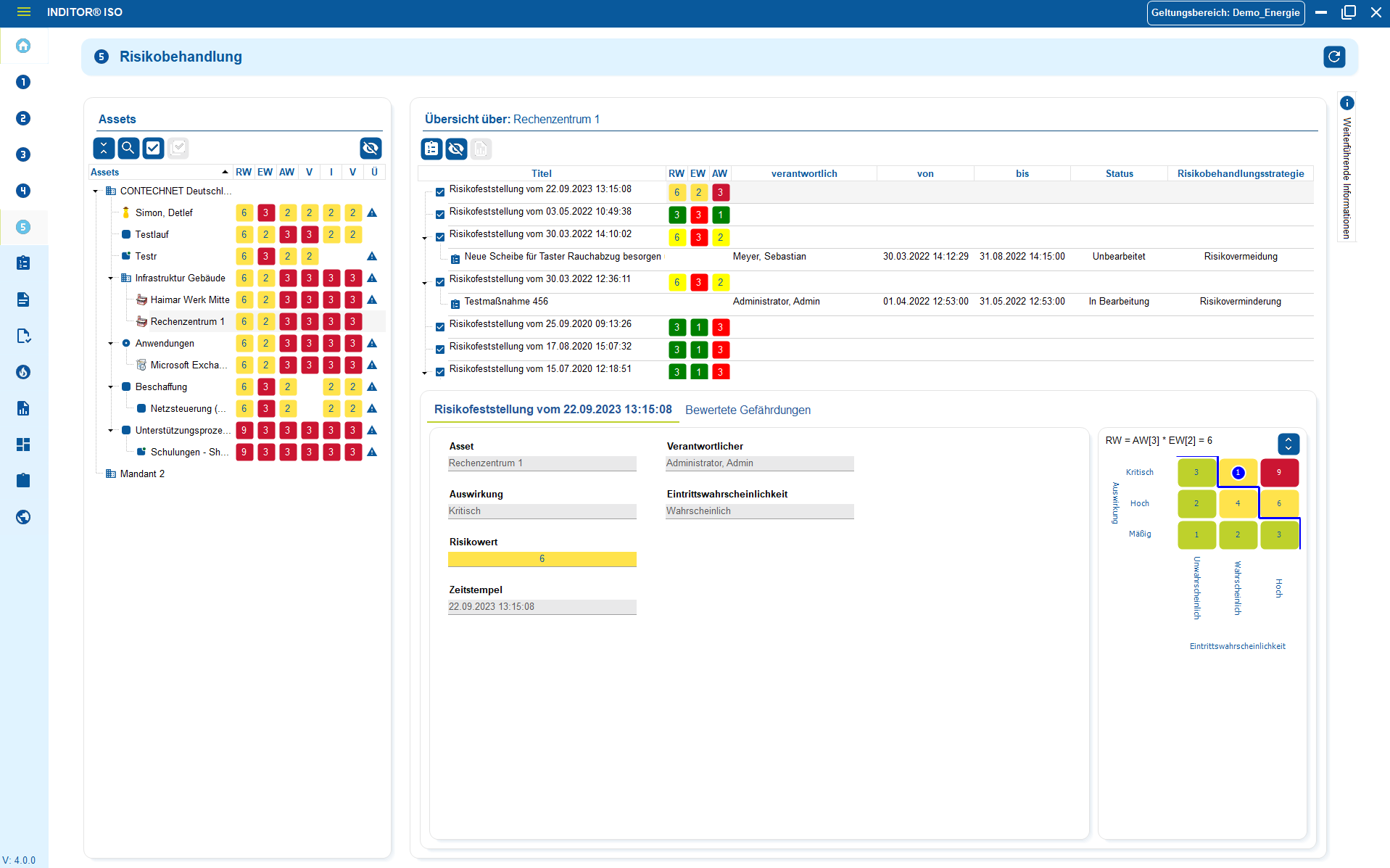
The NIS2 guideline requires structured, traceable and version-controlled documentation of all security-relevant content - from guidelines and organizational procedures to emergency and resilience concepts through to tests, measures and proof of effectiveness.
This documentation must be assigned to clear responsibilities, regularly updated and effective in the context of the actual systems, processes and risks .
A central documentation management system fulfills precisely these requirements:
Guidelines, processes, work instructions, incident logs and audit documents are managed uniformly, versioned and linked directly to assets, risks, measures and responsible parties.
This creates a consistent and auditable documentation basis that meets the requirements of NIS2 audits and regulatory verifications.
Advantages:
- Central storage of all safety-relevant documents: guidelines, emergency concepts, operating procedures, work instructions, protocols and test reports in one place.
- Versioning & historization: Changes are documented in an audit-proof manner - including responsible persons, time stamps and justifications.
- Evidence management for NIS2 inspections: Decisions, measures, incidents and effectiveness assessments are fully traceable.
- Link to assets, risks & measures: Documents do not exist in isolation, but in the context of the actual infrastructure, processes and company-wide responsibilities.
Industries
View all solutions for your industry



Read more



Example use cases
Take a look at further use cases
assets
and system manuals
management
management
and access
1. Import of existing assets
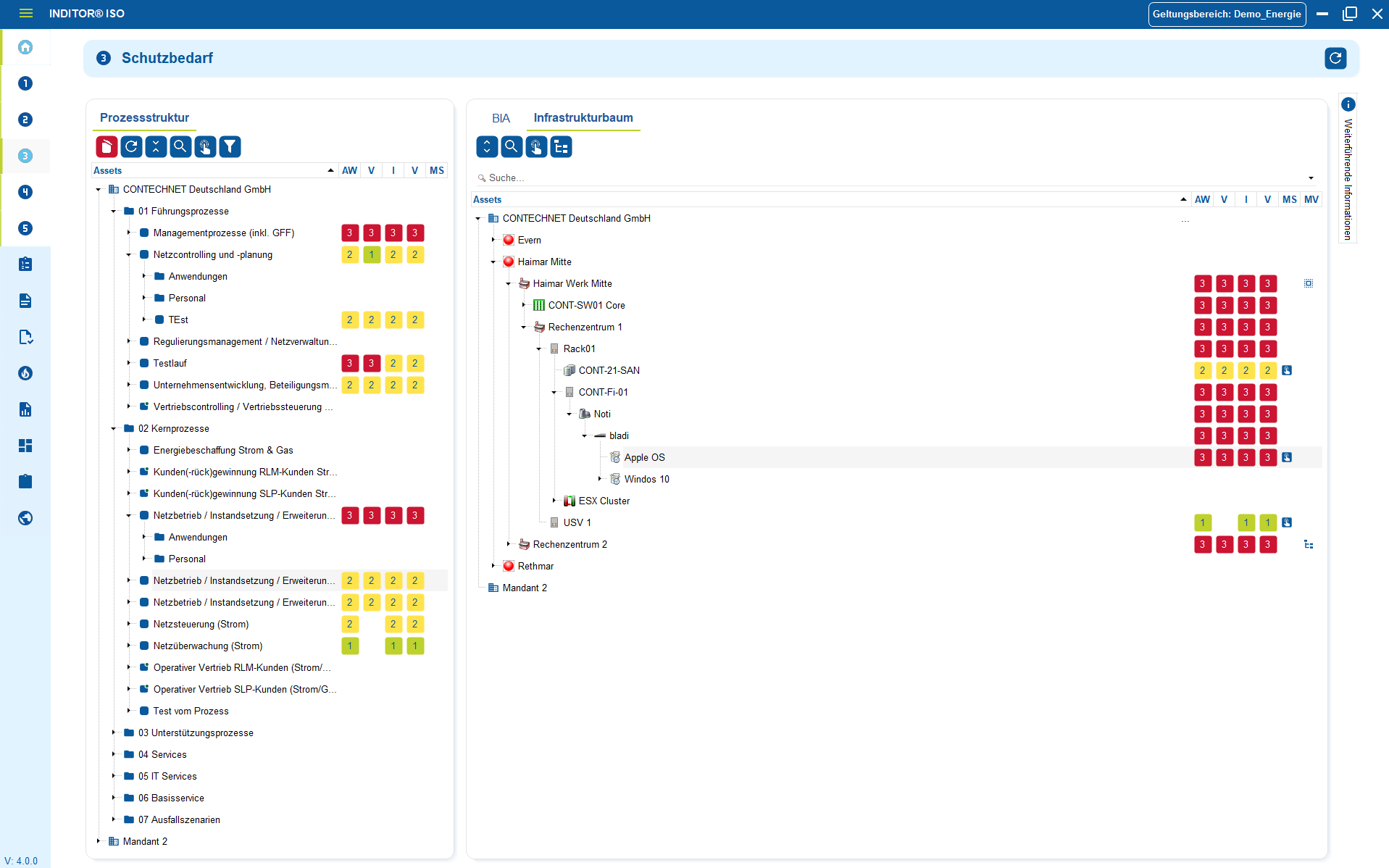
Many companies already have data on systems, applications, locations, contracts or responsibilities. However, it is often scattered across Excel lists, internal repositories, monitoring information or previous inventories. Instead of manually entering this information again, existing structures can be adopted and integrated into a central information security architecture.
The import enables an orderly consolidation of all relevant assets - from technical components, cloud services and process data to roles and responsibilities. During the import process, the data is classified, responsibilities are assigned and dependencies are made visible.
On this basis, protection requirements can be determined, risks assessed and suitable measures assigned in accordance with ISO 27001.
Advantages:
- No starting from scratch: existing information is transferred instead of newly recorded
- Transparency: assets, responsibilities and dependencies are clearly visible
- Structure: classification, protection requirements and risks can be assigned directly
- Traceability: changes are versioned and documented for auditing purposes
- Future-proof: repeatable imports avoid data silos and duplicate maintenance
Image shows: Import your existing assets from Excel or other third-party tools
2. IT concepts, emergency and system manuals
Create, link and maintain operational and emergency documentation in a structured and audit-proof manner.
With our tools, you can create and maintain all important technical documentation in a complete, up-to-date and audit-proof manner. Data changes are automatically transferred to emergency and system manuals, operating concepts and guidelines. These can be linked directly to the associated assets, processes and locations. This means that all documentation is automatically fed with real statuses from the IT landscape and remains permanently consistent.
All relevant information such as responsibilities, operating parameters, dependencies, restart processes and recovery times (RTO/RPO) are maintained and versioned centrally. The connection to infrastructure, applications and services means that documentation is not only maintained, but actively lived and constantly kept up to date. This is one of the most important factors for audits, certifications and operational stability.
Advantages:
- Centralized, versioned and audit-proof documentation
- Clear responsibilities and traceable operating processes
- Audit and audit-proof evidence in accordance with ISO 27001, NIS2 and BSI requirements
- Faster restart times in an emergency thanks to clear, always up-to-date instructions
- Transparent dependencies between systems, processes and services
Picture shows: System and emergency manuals can be generated from the available information. These can be regularly updated and stored in a georedundant manner .
3. Security incident management
Link processes and associated assets
Control IT service processes efficiently and transparently. With the integration of ticket systems in i-doit, you can bundle all processes in one place. From fault reports and change requests to service requests. The link to your assets, contracts and responsibilities creates a central information base for the entire IT operation.
Tickets are documented in a traceable manner, automatically classified and can be prioritized, delegated and closed using defined workflows. This creates a smooth process between technology, organization and support.
Advantages:
- Standardized control of all IT processes
- Clear responsibilities and faster response times
- Seamless traceability of changes and measures
- Direct connection to CMDB objects and documentation
- Basis for key figures, evaluations and process optimization
Image shows: Security incidents can be recorded centrally and included in the risk assessment

4. Supplier management
External service providers, hosting providers, maintenance partners or cloud services are often directly involved in critical business processes. Structured supplier management makes it possible to map their services, risks, contracts and dependencies centrally. Responsibilities, service levels, security requirements and effects on information assets are documented in a traceable manner and linked to the relevant processes and measures.
This allows companies to retain control over which suppliers have access to which information assets, which requirements apply and whether agreed protective measures are being adhered to
Advantages:
- Transparency across all security-relevant suppliers and service providers
- Traceable assignment to assets, processes, locations and risks
- Clear responsibilities, competencies and service levels
- Contractual security requirements and compliance specifications can be documented centrally
- Ready to provide evidence for audits, certifications and regulatory checks
Picture shows: The status of systems, devices and other assets is directly visible in the IT documentation.

5. Control & distribution of tasks and access
A functioning ISMS requires clear responsibilities. Who evaluates measures, who releases risks, who is allowed to change guidelines or who is only allowed to read - all of this determines security, efficiency and auditability.
Finely granulated role and authorization concepts clearly assign responsibilities: Teams, departments and individuals are given exactly the access they need for their tasks. Sensitive information remains protected, operational processes remain transparent and evidence is not diluted.
Advantages:
- Clear responsibilities: Roles and tasks are clearly assigned - no gray areas or duplication of responsibilities.
- Finely granulated access control: Authorizations for objects, categories and processes can be precisely defined.
- Protection of sensitive information: Critical data is only visible and editable for authorized users.
- Auditability through traceability: every action can be traced back in terms of time, organization and personnel.
- Reduced errors and misunderstandings: Teams only work with the information they really need.
Image shows: Audit check with direct links to standard requirements, measures and evidence - fully traceable and auditable.

.png?width=300&name=Contact%20(1).png)
Book your personal live demo
Our i-doit team will be happy to take the time to advise you personally on your application.




