GDPR
Software, use cases & solutions
4.7/5 on Capterra | 2,000+ satisfied customers

What is the GDPR?
Introduction
What is the GDPR?
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) obliges organizations to process personal data in a lawful, secure and traceable manner.
The focus is on accountability, transparency, data security, purpose limitation, data minimization and verifiability - regardless of industry or company size.
The GDPR requires companies to know their data processing, assess risks and implement suitable technical and organizational measures (TOMs).
These include the recording and classification of processing activities, protection requirements, access controls, order processing, emergency and deletion concepts, incident handling and regular reviews of effectiveness.
With suitable software, these requirements can be mapped in a structured manner - from processing directories and data flows to roles and responsibilities, risks, measures, checks and proof of documentation.
This allows companies to implement the GDPR efficiently, comprehensibly and auditably, without scattered tables, Excel lists or manual isolated solutions.
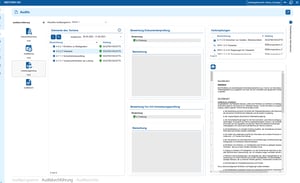
Use cases
Use cases relating to ISMS, risk and compliance management

You control audits centrally, plan audits, document results and automatically generate audit reports.

You can manage documents in an audit-proof manner, version and edit them directly in the tool and use templates and import functions.

i-doit supports GAP analyses according to standards such as ISO 27001, ISO 9001 or NIS2, including maturity level assessment, responsibilities and document assignment.

You evaluate and manage suppliers centrally, document contracts and maintain contact details and replacement suppliers.

You derive measures, distribute tasks, track deadlines and receive automatic notifications by e-mail.

You document and evaluate security incidents in accordance with ISO and NIS2, assign affected assets and centrally derive measures.
Why digitalize data protection?
Why a digital structure is indispensable in data protection
Why digitize data protection?
In everyday life, data protection fails not because of laws, but because of a lack of organization:
Processing is in Excel spreadsheets, DP contracts are somewhere in a mailbox, nobody knows deletion deadlines and nobody knows who has to respond within 72 hours in the event of a data incident.
As soon as a customer or the supervisory authority requests information, the stress begins: "Where are the contracts? Who was responsible? What data was processed? Who has access?"
Without a central location where processing activities, responsibilities, measures and incidents are recorded and tracked, no company can act reliably.
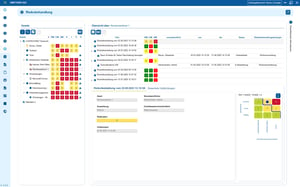
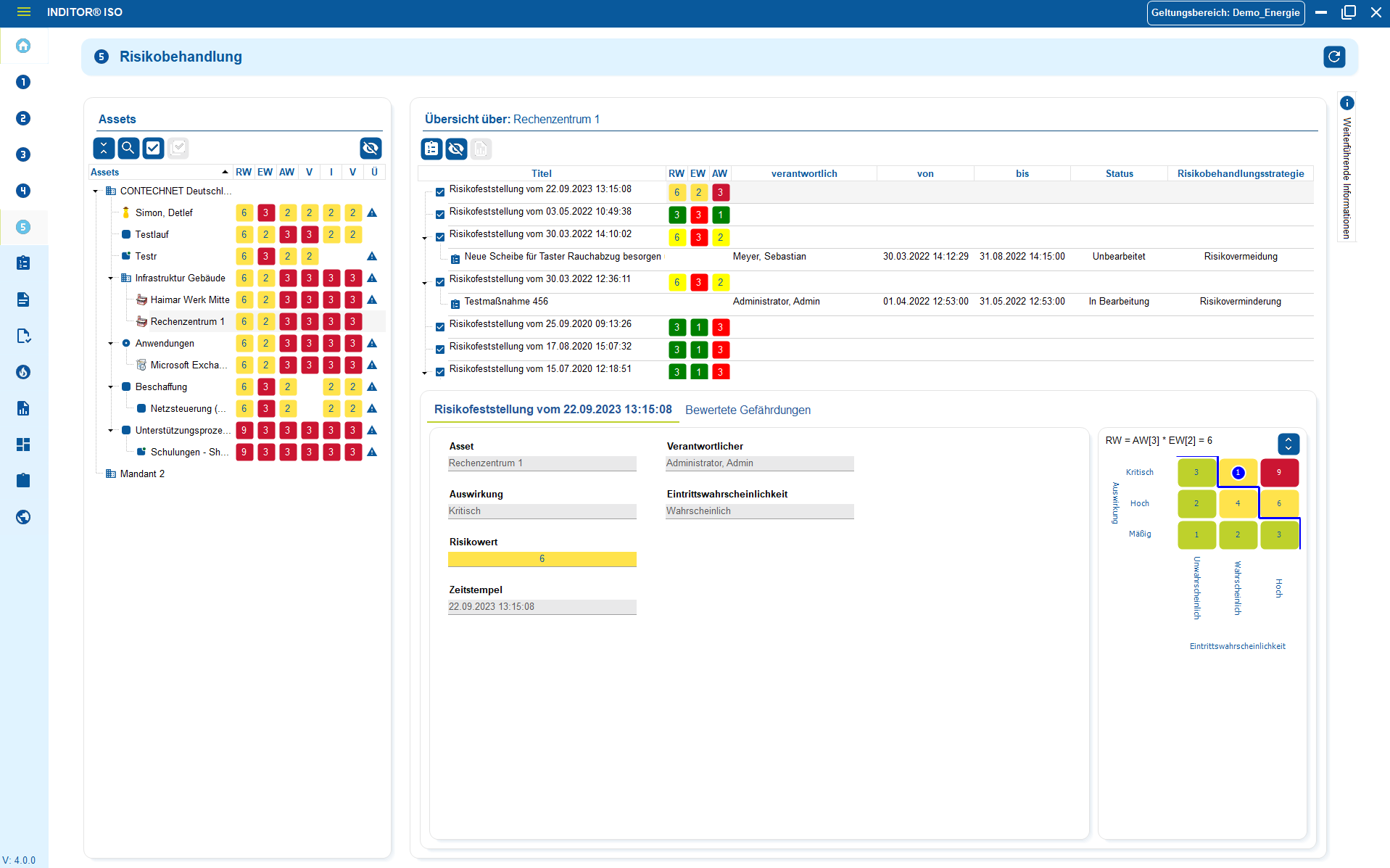
GDPR-compliant in 3 steps
How you can become GDPR-compliant in 3 steps
and document it
implement suitable measures
handle professionally
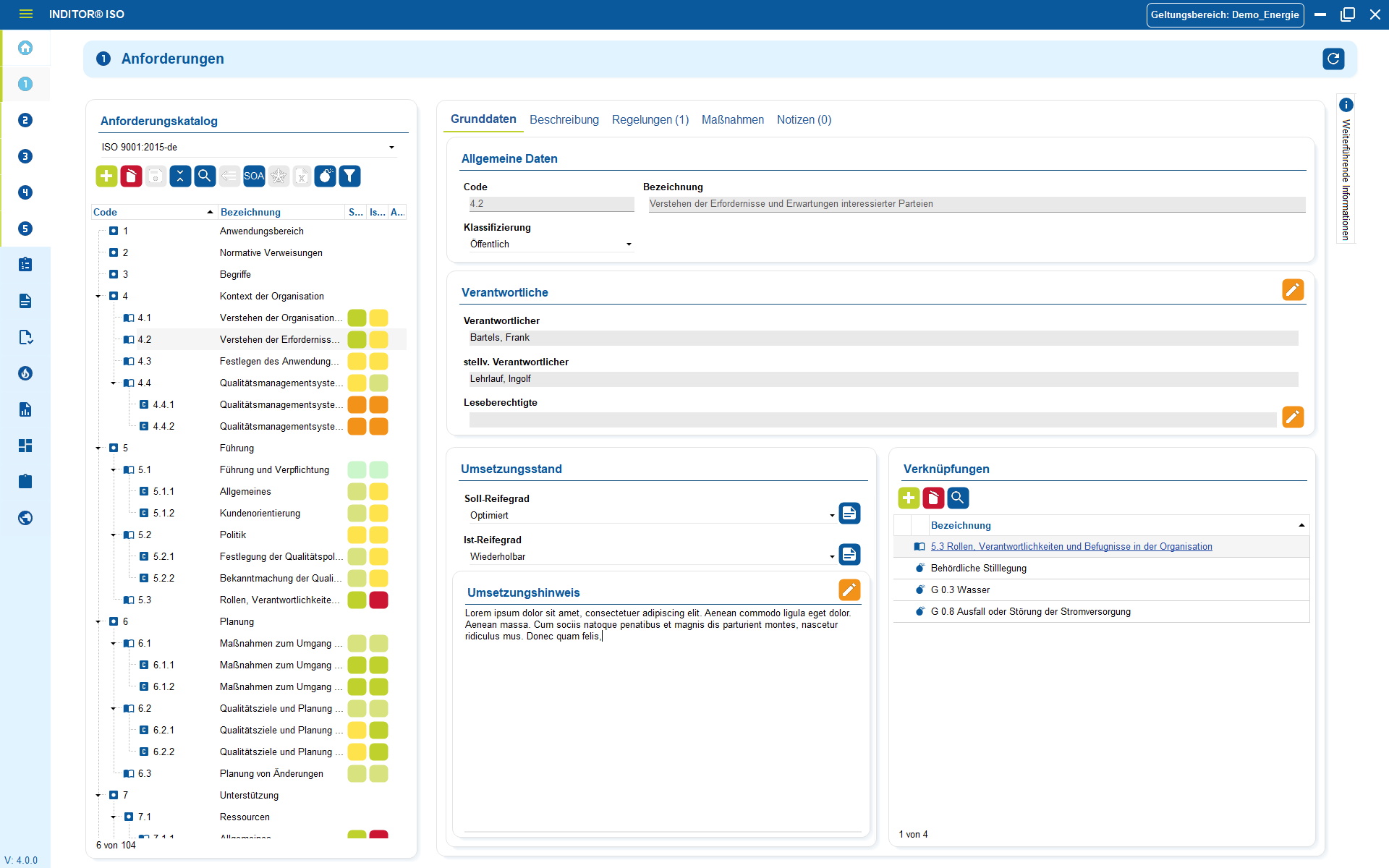
1. Understanding and documenting data processing
The GDPR fails in everyday life not because of legal paragraphs, but because nobody knows where data is located and why it is being processed.
The first step is therefore not about "perfect compliance", but about transparency: What personal data is processed? In which systems? For what purpose? Who has access? And how long does it need to be stored?
Instead of scattered Excel lists, old emails or islands of knowledge, structured documentation is created: processing purposes, data categories, roles, applications, storage locations, deletion periods and service providers.
With this basis, decisions can be made in a justified, comprehensible and legally compliant manner.
Advantages:
- Transparency instead of guesswork: All processing, systems and responsibilities are centrally documented and can be found at any time.
- Practical overview: You know which data is stored where, who has access and on what legal basis it is processed.
- Fast response times: queries from customers, employees or authorities can be answered clearly without having to play "firefighter" within the company.
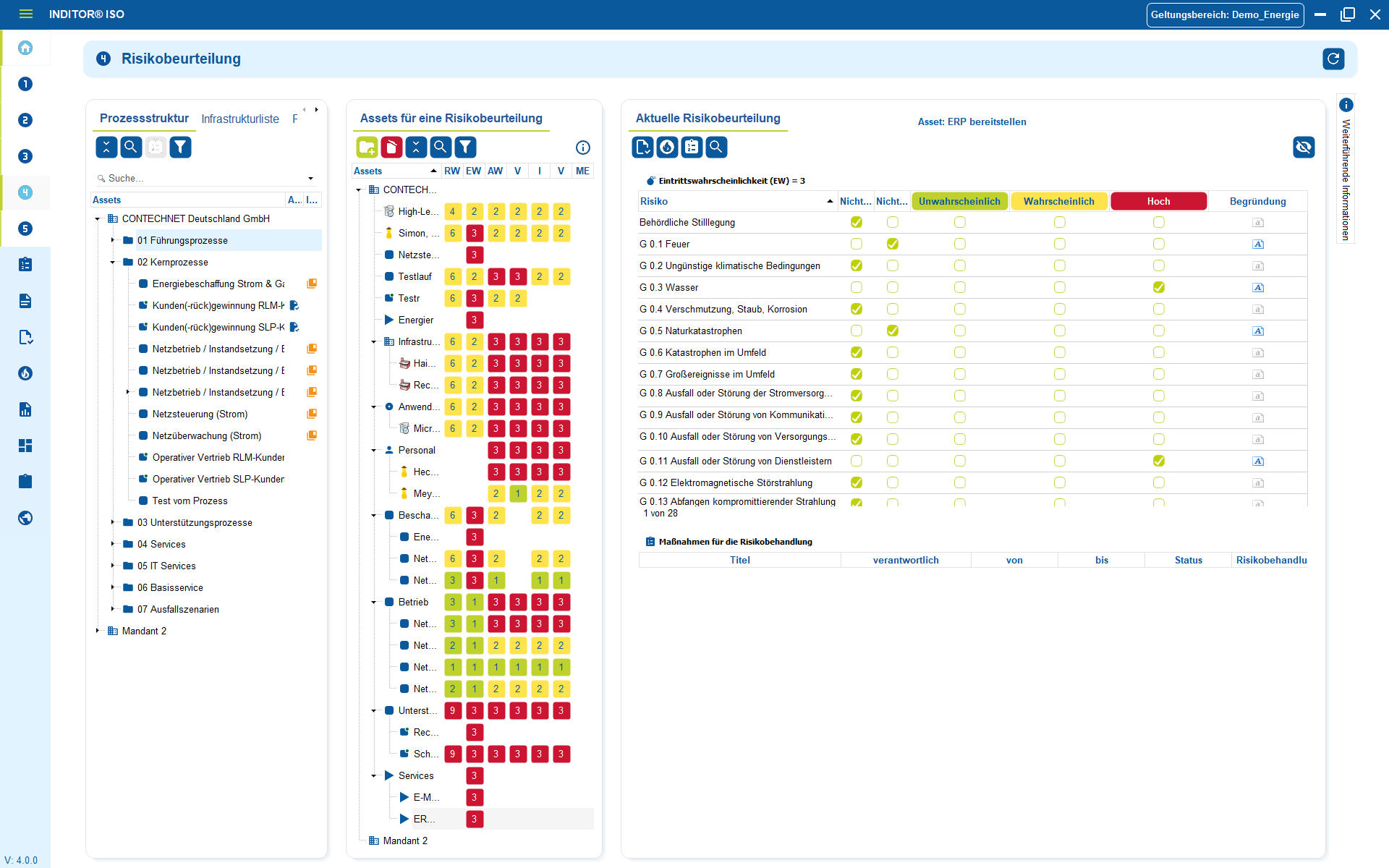
2. Assess risks and implement appropriate measures
GDPR does not require excessive security - it requires appropriate security.
Access concepts, strong authentication, backups, encryption, role models, logging, training - not everything has to happen at the same time, but each topic must be justified and demonstrably addressed.
It is not the length of the list of measures that is important, but the connection between: risk → measure → effectiveness.
A company that documents these three points can not only explain what it is doing in an emergency, but also why it made the decision it did and how the measures work.
This is precisely what protects against fines, loss of customers and lengthy disputes with the authorities.
Advantages:
- Appropriate rather than random safety measures: Decisions are based on real risks - not gut feelings or marketing promises from tool providers.
- Demonstrable effectiveness: Each measure has a purpose, a responsible party and a point at which it is checked to see if it works.
- Fewer costly mistakes: Vulnerabilities are identified before the incident - not afterwards when data has already been leaked.
3. Handle incidents and data protection requests professionally
The moment of truth doesn't come when everything is going well - but when something goes wrong.
A loss of data, unwanted access, a misconfigured cloud service or an incorrect email can become a problem in minutes.
But what to do?
Incidents are assessed, documented and reported to the right place before deadlines expire or information disappears. The same applies to data subject rights: inquiries are recorded, checked and answered - not lost between the CRM, ticket system and employee mailbox.
A company that processes incidents and requests in a controlled manner saves time and retains credibility.
Advantages:
- Fast response time: Whether incident or request - there is a defined process, responsibilities and deadlines.
- Proven professionalism: Procedures and decisions are documented - this reduces the risk of sanctions and reputational damage.
- Fewer repeat errors: Every incident provides insights that are incorporated into better measures - real improvement instead of reactive firefighting.
Industries
View all solutions for your industry



Read more



Example use cases
Take a look at further use cases
assets
and system manuals
management
management
and access
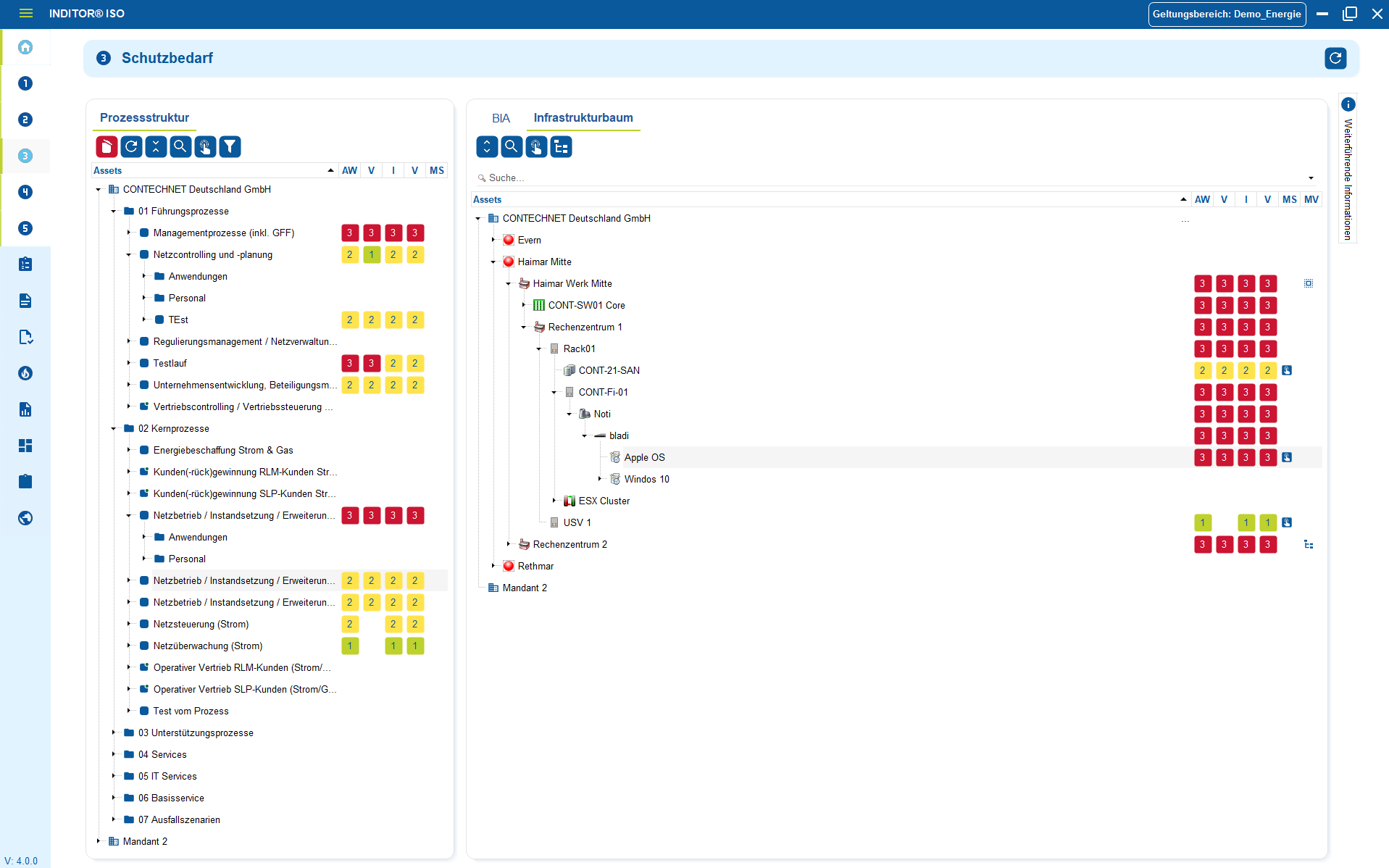
1. Import of existing assets
Many companies already have data on systems, applications, locations, contracts or responsibilities. However, it is often scattered across Excel lists, internal repositories, monitoring information or previous inventories. Instead of manually entering this information again, existing structures can be adopted and integrated into a central information security architecture.
The import enables an orderly consolidation of all relevant assets - from technical components, cloud services and process data to roles and responsibilities. During the import process, the data is classified, responsibilities are assigned and dependencies are made visible.
On this basis, protection requirements can be determined, risks assessed and suitable measures assigned in accordance with ISO 27001.
Advantages:
- No starting from scratch: existing information is transferred instead of newly recorded
- Transparency: assets, responsibilities and dependencies are clearly visible
- Structure: classification, protection requirements and risks can be assigned directly
- Traceability: changes are versioned and documented for auditing purposes
- Future-proof: repeatable imports avoid data silos and duplicate maintenance
2. IT concepts, emergency and system manuals
Create, link and maintain operational and emergency documentation in a structured and audit-proof manner.
With our tools, you can create and maintain all important technical documentation in a complete, up-to-date and audit-proof manner. Data changes are automatically transferred to emergency and system manuals, operating concepts and guidelines. These can be linked directly to the associated assets, processes and locations. This means that all documentation is automatically fed with real statuses from the IT landscape and remains permanently consistent.
All relevant information such as responsibilities, operating parameters, dependencies, restart processes and recovery times (RTO/RPO) are maintained and versioned centrally. The connection to infrastructure, applications and services means that documentation is not only maintained, but actively lived and constantly kept up to date. This is one of the most important factors for audits, certifications and operational stability.
Advantages:
- Centralized, versioned and audit-proof documentation
- Clear responsibilities and traceable operating processes
- Audit and audit-proof evidence in accordance with ISO 27001, NIS2 and BSI requirements
- Faster restart times in an emergency thanks to clear, always up-to-date instructions
- Transparent dependencies between systems, processes and services
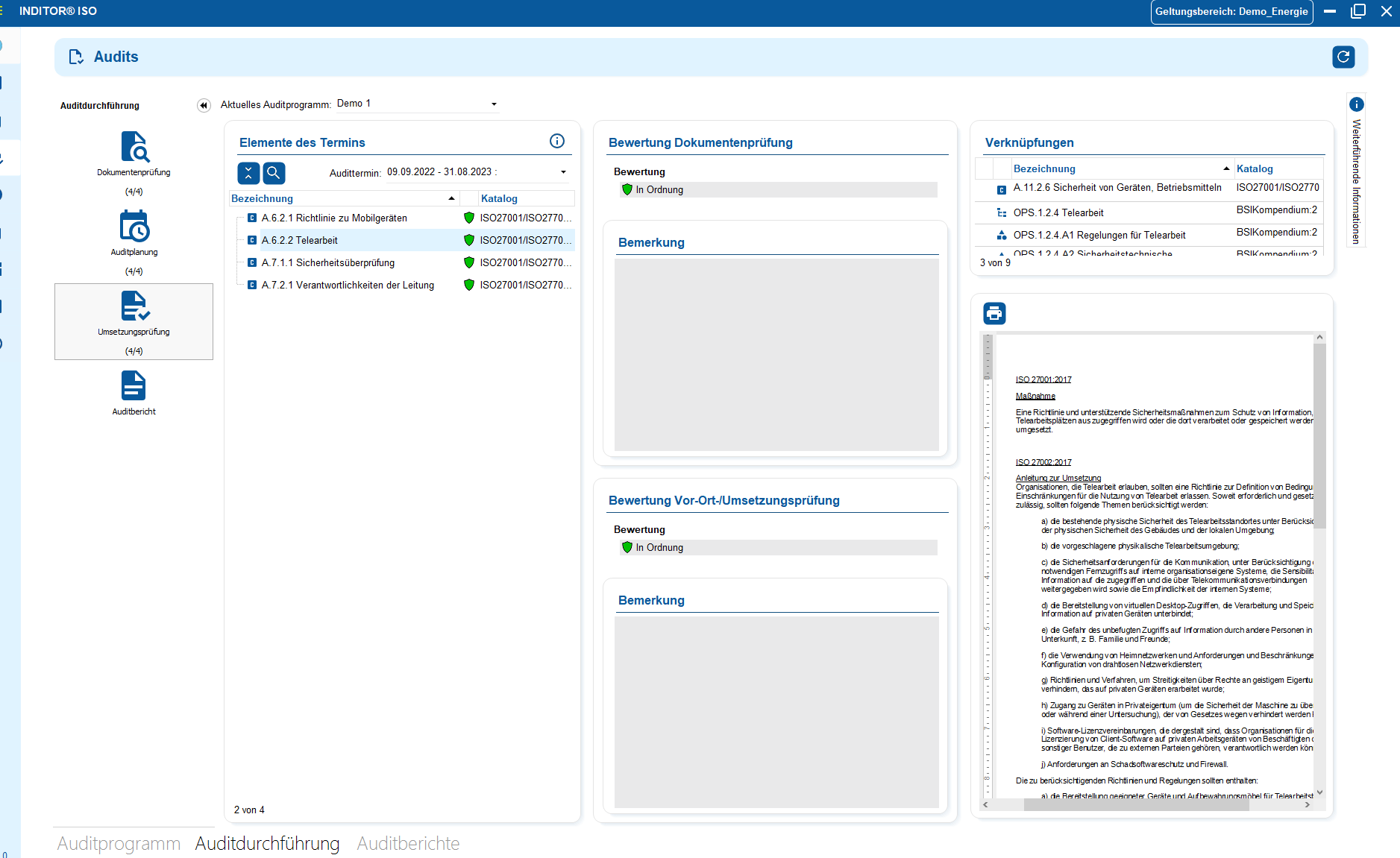
3. Security incident management
Link processes and associated assets
Control IT service processes efficiently and transparently. With the integration of ticket systems in i-doit, you can bundle all processes in one place. From fault reports and change requests to service requests. The link to your assets, contracts and responsibilities creates a central information base for the entire IT operation.
Tickets are documented in a traceable manner, automatically classified and can be prioritized, delegated and closed using defined workflows. This creates a smooth process between technology, organization and support.
Advantages:
- Standardized control of all IT processes
- Clear responsibilities and faster response times
- Seamless traceability of changes and measures
- Direct connection to CMDB objects and documentation
- Basis for key figures, evaluations and process optimization

4. Supplier management
External service providers, hosting providers, maintenance partners or cloud services are often directly involved in critical business processes. Structured supplier management makes it possible to map their services, risks, contracts and dependencies centrally. Responsibilities, service levels, security requirements and effects on information assets are documented in a traceable manner and linked to the relevant processes and measures.
This allows companies to retain control over which suppliers have access to which information assets, which requirements apply and whether agreed protective measures are being adhered to
Advantages:
- Transparency across all security-relevant suppliers and service providers
- Traceable assignment to assets, processes, locations and risks
- Clear responsibilities, competencies and service levels
- Contractual security requirements and compliance specifications can be documented centrally
- Ready to provide evidence for audits, certifications and regulatory checks

5. Control & distribution of tasks and access
A functioning ISMS requires clear responsibilities. Who evaluates measures, who releases risks, who is allowed to change guidelines or who is only allowed to read - all of this determines security, efficiency and auditability.
Finely granulated role and authorization concepts clearly assign responsibilities: Teams, departments and individuals are given exactly the access they need for their tasks. Sensitive information remains protected, operational processes remain transparent and evidence is not diluted.
Advantages:
- Clear responsibilities: Roles and tasks are clearly assigned - no gray areas or duplication of responsibilities.
- Finely granulated access control: Authorizations for objects, categories and processes can be precisely defined.
- Protection of sensitive information: Critical data is only visible and editable for authorized users.
- Auditability through traceability: every action can be traced back in terms of time, organization and personnel.
- Reduced errors and misunderstandings: Teams only work with the information they really need.

.png?width=300&name=Contact%20(1).png)
Book your personal live demo
Our i-doit team will be happy to take the time to advise you personally on your application.




