ITIL
Software, use cases & solutions
4.7/5 on Capterra | 2,000+ satisfied customers

What is ITIL?
ITIL (Information Technology Infrastructure Library) is a globally recognized framework that defines how IT services are planned, provided, operated and continuously improved.
In contrast to purely operational IT processes, ITIL creates a holistic standard for service quality, responsibilities, value creation and risk minimization - regardless of company size or industry.
ITIL not only answers "How do we solve IT problems?", but also "How do we create long-term stable IT operations with clear roles, repeatable processes and measurable results?"
It ensures that service delivery, incident management, changes, maintenance, operation and improvement are not dependent on individuals, but are based on documented procedures.
ITIL creates a link between business and IT:
IT does not deliver an end in itself, but supports specific business objectives, SLAs, customer expectations and regulatory requirements.
The framework reduces risks, lowers operating costs, prevents failures and increases availability because decisions are made systematically rather than reactively.
Use cases
Use cases relating to ISMS, risk and compliance management

You control audits centrally, plan audits, document results and automatically generate audit reports.

You can manage documents in an audit-proof manner, version and edit them directly in the tool and use templates and import functions.

i-doit supports GAP analyses according to standards such as ISO 27001, ISO 9001 or NIS2, including maturity level assessment, responsibilities and document assignment.

You evaluate and manage suppliers centrally, document contracts and maintain contact details and replacement suppliers.

You derive measures, distribute tasks, track deadlines and receive automatic notifications by e-mail.

You document and evaluate security incidents in accordance with ISO and NIS2, assign affected assets and centrally derive measures.
ITIL - Plan, operate and improve services in a structured way
ITIL provides the framework for viewing IT services not as individual technical components, but as a complete value proposition. i-doit does not map these services theoretically, but links them to real company objects - servers, clients, network components, licenses, responsible parties, contracts and dependencies.
This creates traceable service chains: from the request, provision and operation to maintenance and decommissioning. Decisions are not based on gut feeling or the knowledge of individual employees, but on a consistent CMDB basis.
Advantages:
- Transparent service architecture: Services are not only described, but also linked to assets, roles and processes.
- Standardized processes: ITIL processes such as incident, change or request fulfillment draw directly on documented infrastructure and are not detached from each other.
- Continuous improvement: Histories, dependencies and service metrics create a reliable basis for optimization instead of reacting to individual problems.
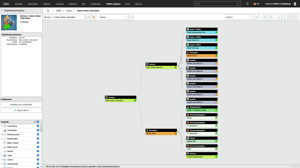
With i-doit, you can see relationships and dependencies between systems, applications, contracts, people and other assets
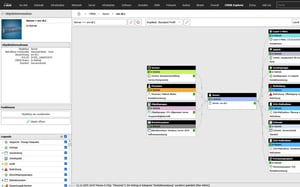
Ticketing
Link processes, faults and tasks directly to assets
By connecting a ticket system, i-doit becomes the central source of information for IT support. When a ticket is created, all relevant data on the affected device, user or service is immediately available - including history, faults, software versions and contracts. Processes can be linked directly to the associated assets so that support and technology work with the same database. The bidirectional exchange automatically keeps all information up to date and reduces manual effort.
Advantages:
- Faster error analysis: All relevant asset and user information is directly available with the ticket, which means that causes can be identified more quickly.
- Standardized information: Support, technology and management work with the same database thanks to the direct linking of tickets and CMDB objects.
- Automated up-to-dateness: Bidirectional synchronization keeps master data, status and changes up to date without manual effort.
Tickets can be linked directly to assets in i-doit in order to list all associated processes in a structured manner.
IT asset management and discovery
Automated network inventory for consistent data quality and minimized maintenance effort
A discovery tool automatically inventories your network and keeps the CMDB i-doit up to date without any manual effort. Devices, changes and new systems are recognized, transferred in a structured manner and assigned directly to the appropriate objects. Shadow IT becomes visible, data remains consistent and the maintenance effort is significantly reduced.
Advantages:
- Automatic updating: New devices and changes are adopted directly without manual maintenance.
- Increased transparency: Hidden systems and shadow IT are visible and clearly documented.
- Significantly less effort: Inventory, reconciliation and updates run in the background with minimal personnel input.
Monitoring
Operating states and events in the context of documentation
Monitoring systems determine the status of systems and services in real time. Thanks to the link with i-doit, these statuses are not viewed in isolation, but in the context of the documented assets.
Warnings, threshold values and availabilities therefore relate to specific devices, servers, applications or network segments. The collected status information supplements the documentation and forms a reliable basis for planning, troubleshooting and service quality.
Advantages:
- Current operating data visible on the affected assets
- Identification of faults with reference to locations or dependencies
- Conclusions on bottlenecks or recurring faults
- Support for trend analyses, maintenance cycles and capacity planning
With the CMDB Explorer, you can see all existing relationships and dependencies for all assets.
Industries
View all solutions for your industry



Read more



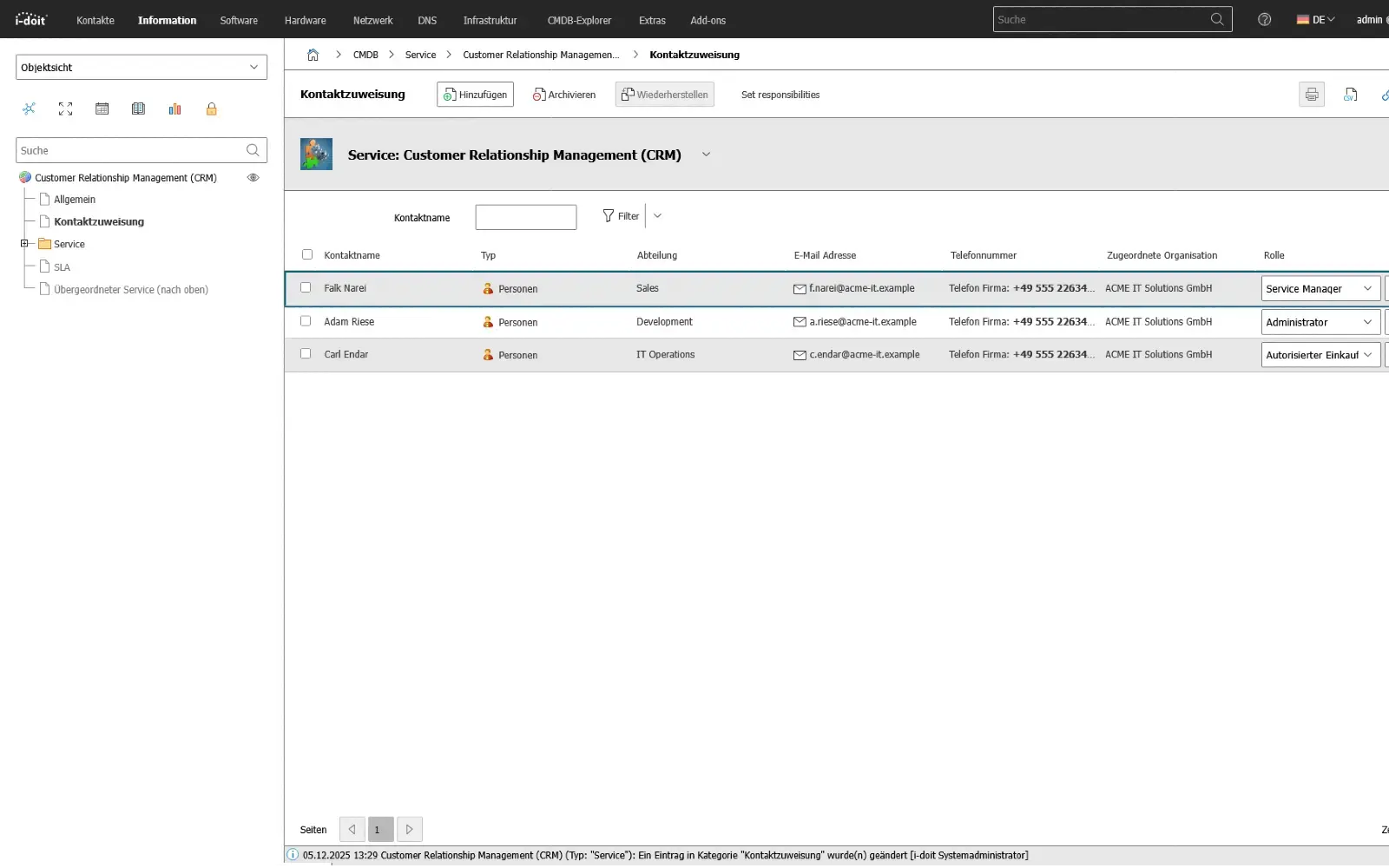
How to use i-doit as a central tool for ITIL-based IT service management
responsibilities according to ITIL
the CMDB
from the documentation
1. Record services, infrastructure and responsibilities according to ITIL
The first step is not just to document individual devices, but to map the IT landscape as ITIL sees it: as services with an underlying infrastructure. In i-doit, services, supporting systems, applications, locations, user groups and suppliers are created as separate objects with clearly defined attributes and linked to each other.
Roles, responsibilities and escalation paths can be assigned directly so that the technology behind each service, who is operationally responsible and what dependencies exist are visible. This creates a CMDB that not only manages inventory data, but also maps the technical view of IT service management.
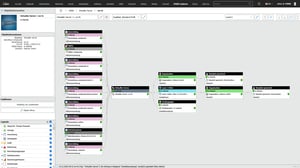
2. Structure ITIL processes on the basis of the CMDB
In the second step, the central ITIL processes such as Incident Management, Change Management, Request Fulfillment or Problem Management are based on the existing documentation. Processes no longer refer only to tickets or numbers, but to specific services and the assets assigned to them in i-doit.
Faults, changes and service requests can thus be evaluated specifically in context. Effects on dependent systems, locations or user groups are immediately recognizable because the underlying structure is already documented. Decisions in the processes are therefore based on verified information instead of individual knowledge or manual lists.
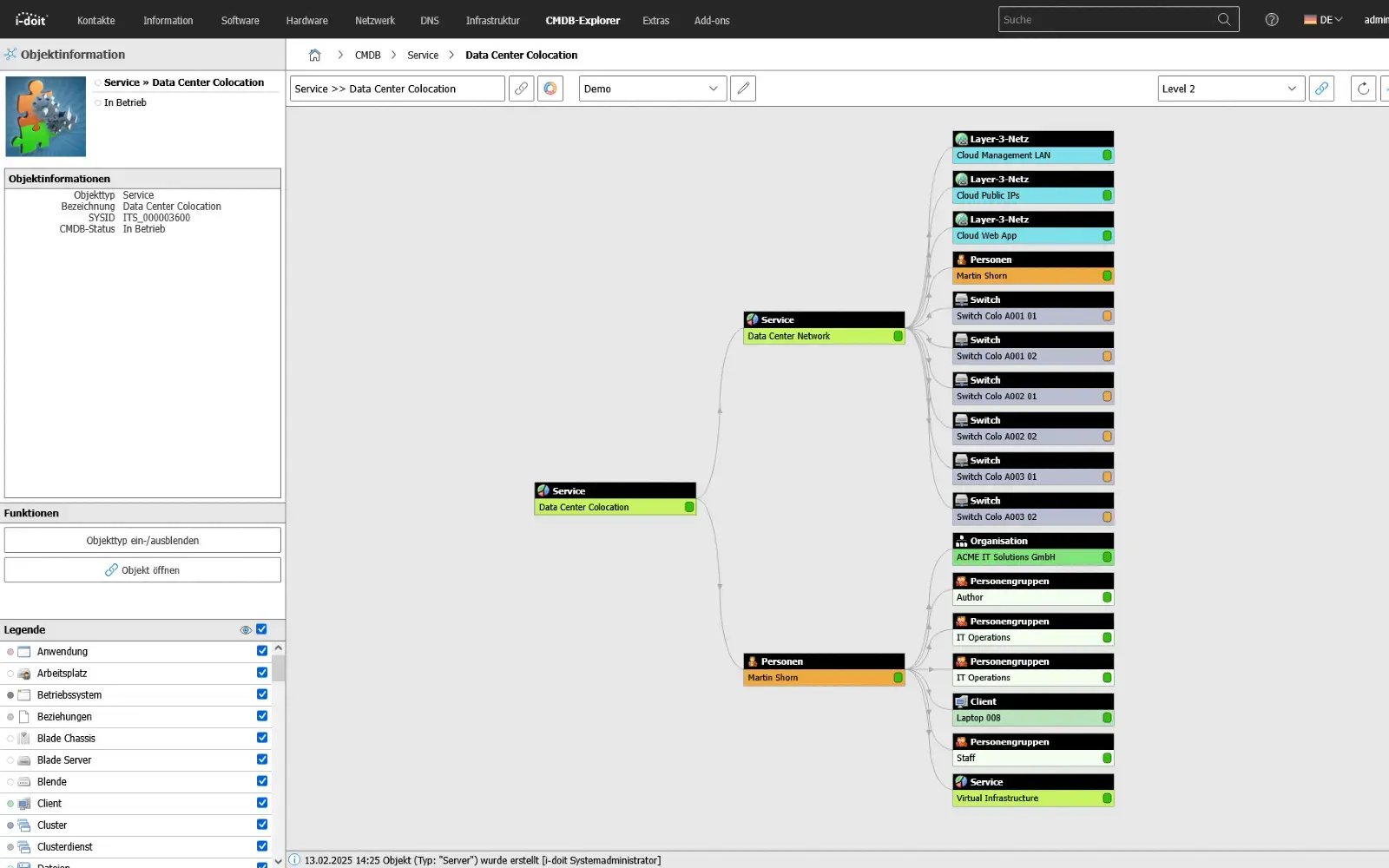
3. Serive service quality, SLAs and improvements from the documentation
In the third step, the documentation is actively used to control and improve service quality. Recurring faults, high-risk changes or bottlenecks in certain services become visible via histories, links and evaluations. Monitoring and ticket data can be combined with the documented services to identify availability, SLA fulfillment and typical problem areas.
On this basis, measures for stabilization or optimization can be planned and tracked. ITIL is therefore not understood as a theoretical framework, but as a continuous improvement process based on the service and infrastructure mapping created in i-doit.
Record key figures and response times for SLAs and OLAs
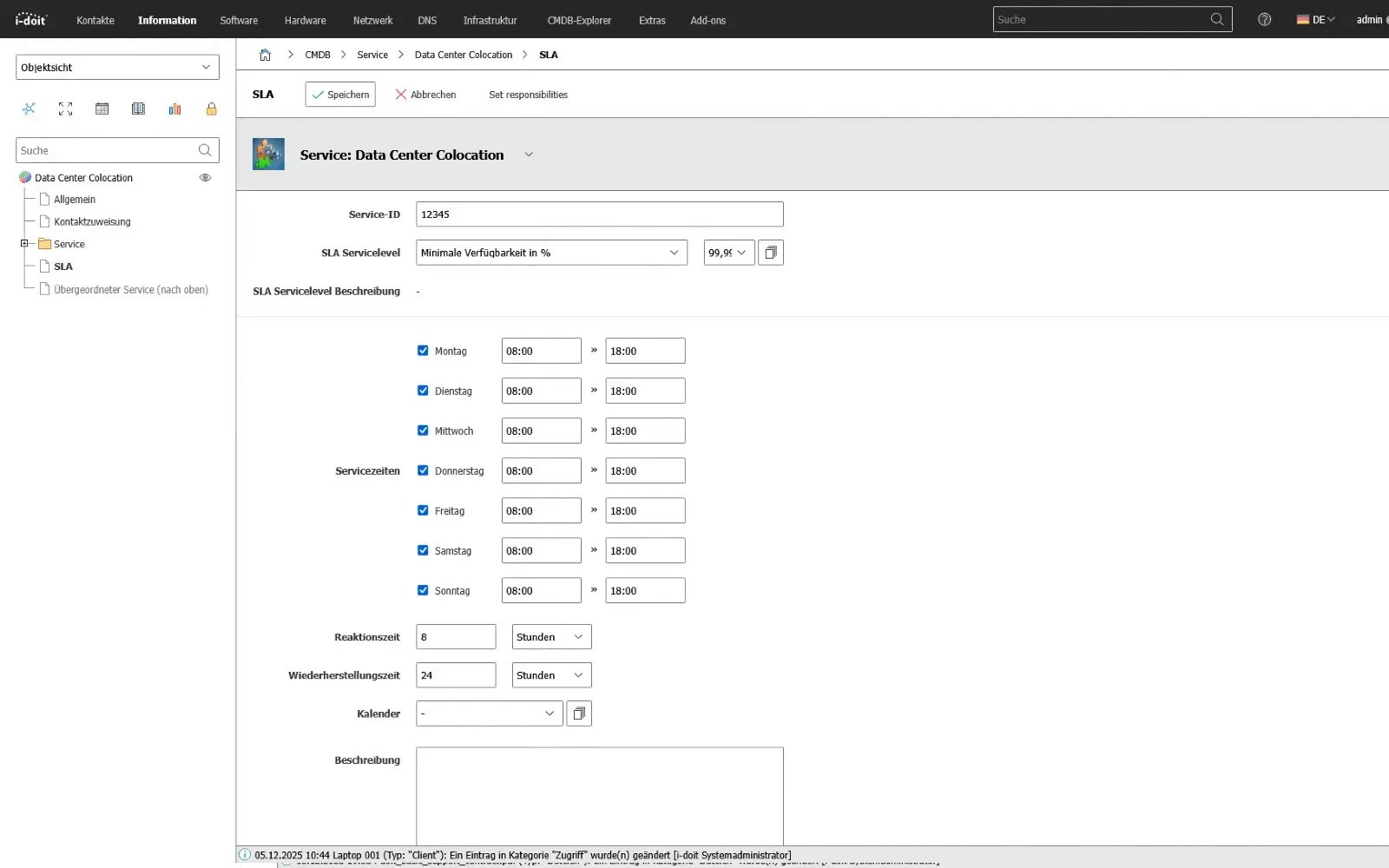
Further use cases for the implementation of ITIL-compliant processes
(Change Tracking)
and authorizations
service lifecycle
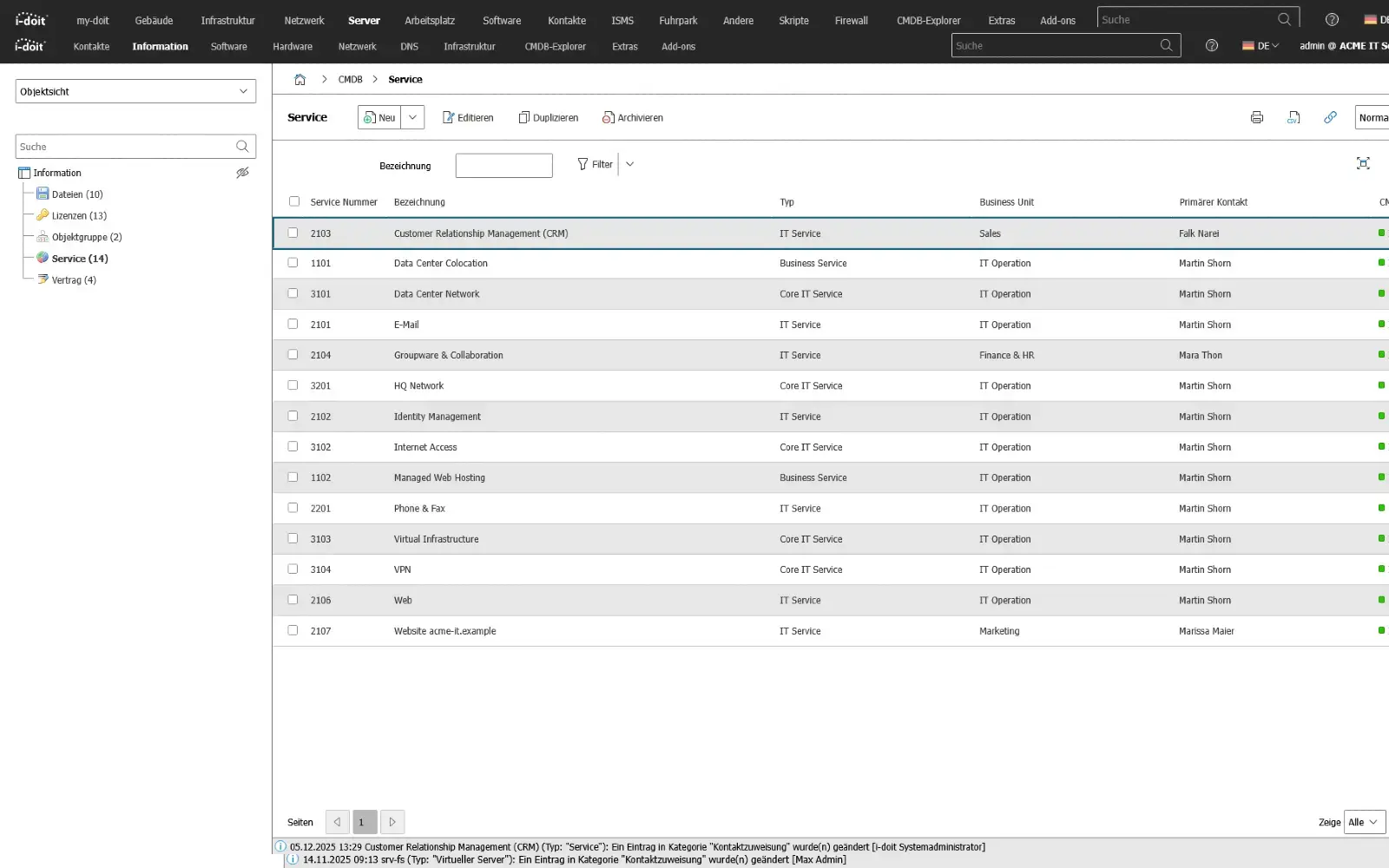
IT service catalog
A service catalog clearly defines which services IT provides, to whom they apply and under which conditions they can be used.
Instead of processing loose requests or private workflows, services are standardized: from workstation setup to database access. Departments know what they can order, what costs are incurred, who is responsible and what service is guaranteed.
A structured service catalog prevents shadow IT, reduces queries and creates certainty of expectations.
IT teams no longer work reactively, but deliver traceable services with agreed targets - regardless of whether they are provided internally or purchased externally.
Advantages:
- Clearly defined services instead of individual tickets
- Transparency regarding costs, responsibilities and provision times
- Reduced coordination and clarification processes
- Expectation management between IT and specialist departments
- Basis for SLAs and service improvements
Change tracking
Changes are one of the biggest risk factors in IT operations - updates, migrations, configurations or new services can bring entire systems to a standstill.
With traceable change tracking, changes are planned, evaluated and documented: Which systems are affected, why was the change carried out, what plan exists in the event of an error, and who approved it?
The entire change history is therefore not just a log, but an operational learning basis:
Impacts, error patterns, rollback experiences and time windows become a knowledge archive over time, which makes subsequent releases more secure and reduces risks.
Advantages:
- Reproducible changes instead of improvised interventions
- Minimized risk of failure through backout and test strategies
- Transparent responsibilities and approvals
- Better planning of maintenance windows
- Traceable effects for operations, audit and compliance
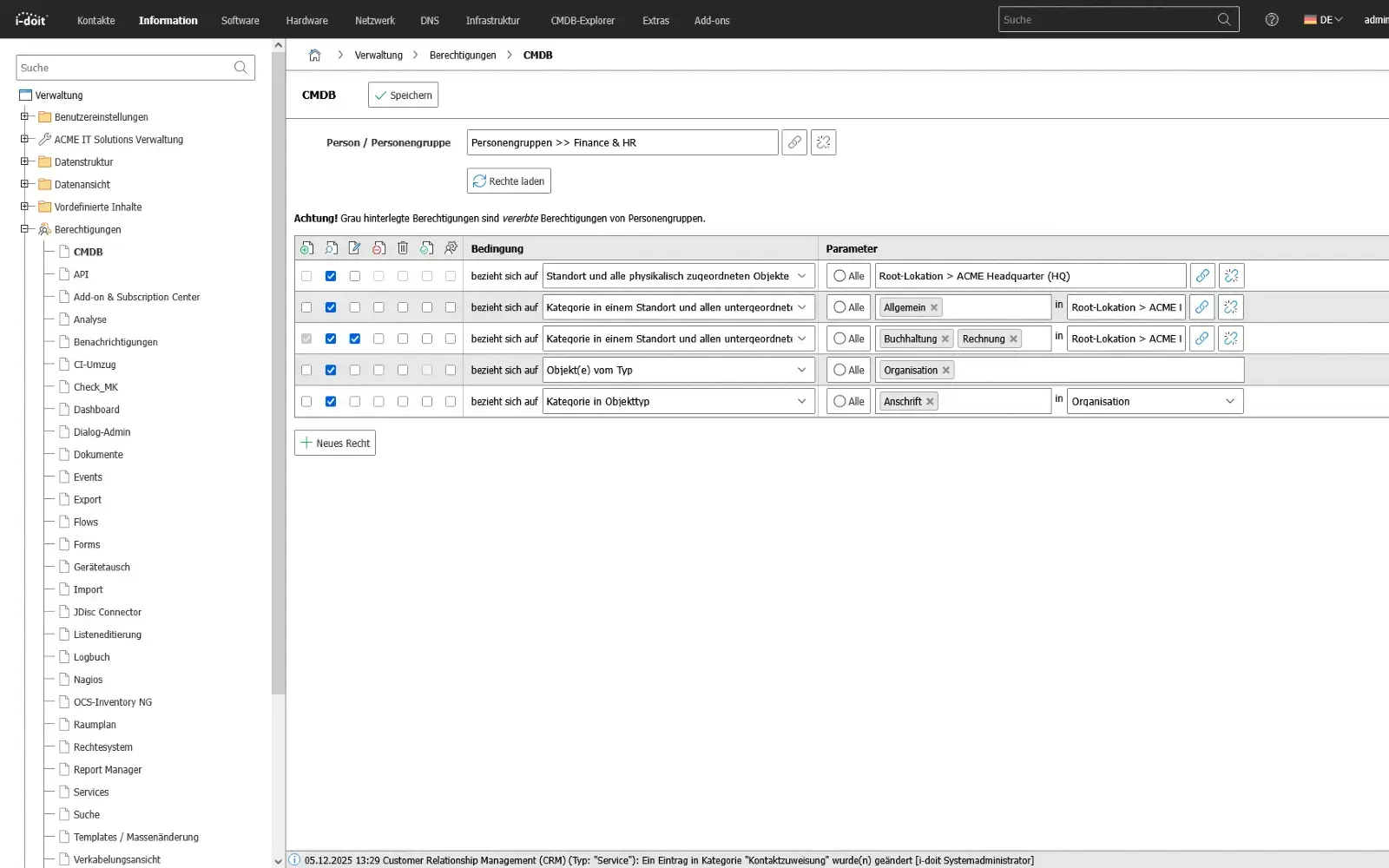
Roles, access and authorizations
Access is not just a technical issue, but also an organizational risk.
A lack of rights stops production processes, too many rights open up security gaps.
Authorizations must therefore not be distributed on the basis of persons, but on the basis of roles, services and responsibilities - with clearly defined handovers for changes, departments or projects.
A structured authorization model makes it possible to delegate responsibilities transparently and, in the event of an audit, to prove without discussion who had access to what and why.
Instead of manually maintaining user lists, a system is created that links rights structures with business processes.
Advantages:
- Risks reduced through role-based access instead of individual decisions
- Traceable changes during onboarding, changes and offboarding
- Clear separation of technical and organizational authorizations
- Audit-proof documentation without loss of knowledge
- Consistent authorization across teams, locations and systems
Asset and service lifecycle
Every IT service has a life cycle: introduction, operation, optimization and shutdown.
Not every service is operated indefinitely, and not every tool is sustainable in the long term.
ITIL therefore treats services like products: They are designed, evaluated, provided, improved and finally decommissioned in a controlled manner.
The service lifecycle prevents systems from "simply continuing to run" until they become a risk.
Planned transitions reduce technical debt, secure operating costs, avoid disruptions and create room for modernization without operational interruptions.
Benefits:
- Planned introduction and controlled shutdown instead of spontaneous migration
- Reduction of technical debt through active further development
- More economical investment decisions over the entire life cycle
- Less operational risk, as outdated services do not "drag on"
- Continuous improvement with measurable results
.png?width=300&name=Contact%20(1).png)
Book your personal live demo
Our i-doit team will be happy to take the time to advise you personally on your application.
Integrations
i-doit can be seamlessly connected to IT service desk systems to optimize your support processes. Examples of compatible systems are ((OTRS)) Community Edition, KIX Service Management and Zammad.
Thanks to its flexible API, i-doit can be integrated with numerous software solutions, including ERP systems.
To automatically add data and assets to your i-doit system, we recommend the use of specialized inventory systems such as JDisc or OCS.
With i-doit, you can document your network topology clearly and in detail and include integrations.
For centralized and secure user and rights management, i-doit can be integrated into directory services such as LDAP or Active Directory.
i-doit is made for the joint operation of monitoring systems. Examples here are: Nagios or Checkmk.
Suitable add-ons
Our add-ons for modular function expansion
Create powerful automations without programming knowledge, simply start them on a schedule or manually at the touch of a button.
Get 4 powerful add-ons for the price of 2! Flows, Documents, Analysis and Forms.
Automatically create documents as PDFs with daily updated data (e.g. hardware handover certificate or disaster recovery plan).
Automate the operation of your data center with the latest data from the CMDB. Events trigger and control further processes.
The maintenance add-on supports the planning, execution and documentation of maintenance and inspections. Maintenance intervals, dates and responsibilities are managed centrally and linked directly to the respective devices, installations or systems.
With the API add-on, data can be automatically read, written and updated in i-doit. Perfect for integrations with ticket systems, inventory tools or your own automations.
Add-on for powerful data analysis. Calculate service costs, check the data quality of the CMDB and carry out failure simulations.
Easily create forms that you can make available to users for simplified data entry. Example: Allow users to document hardware or goods themselves.
Set up an information security management system with risk analysis and management in accordance with ISO 27001.
Integrate the Checkmk2 monitoring system into i-doit. This supports comparisons between TARGET and ACTUAL from CMDB and monitoring.
Store buttons with your own triggers and start IT processes directly from i-doit - e.g. the automatic deployment of a virtual machine.
With this add-on, you can create an information security management system (ISMS) in accordance with the BSI's IT baseline protection methodology.




